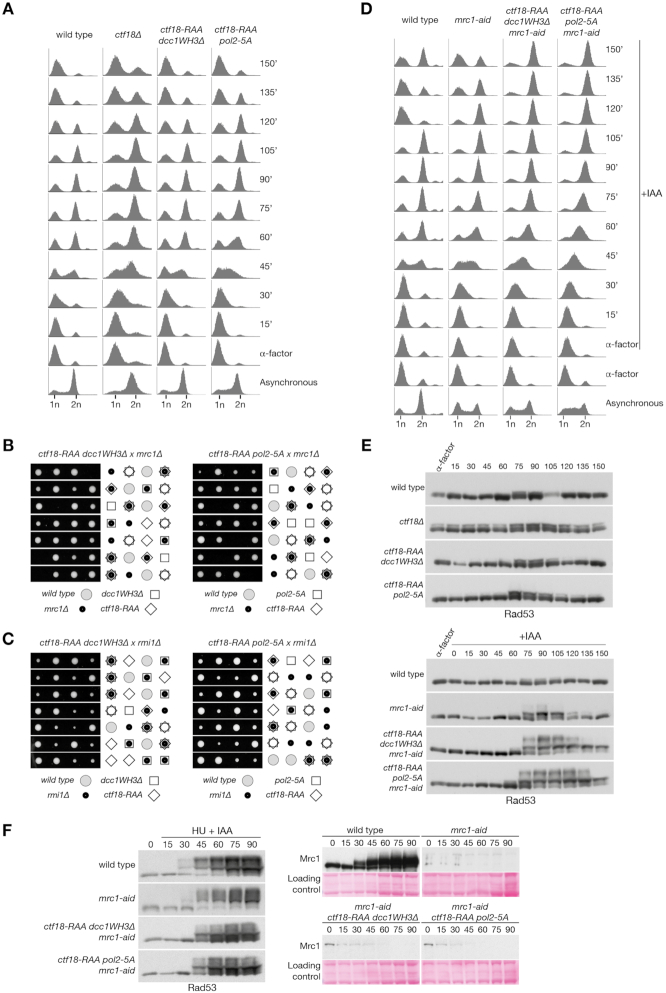
Figure 6.
Mrc1 is essential for viability in the absence of the Ctf18-RFC/Pol ϵ interaction. (A) FACS analysis of DNA replication during a single cell cycle. The indicated strains were grown to exponential phase at 24°C, arrested in G1 and synchronously released. α-factor was added back 30 minutes after release to block entry in the next cell cycle. (B, C) Tetrad analysis of the meiotic progeny of the diploid strains indicated, showing synthetic lethality between ctf18-RAA dcc1WH3Δ/pol2-5A and mrc1Δ (B), but not rmi1Δ (C). (D) FACS analysis of DNA replication during a single cell cycle. The strains were treated as for panel A, except for the incubation for 1 h in G1 with 0.5 mM IAA final concentration to induce the degradation of mrc1-aid and the release in medium containing 0.5 mM IAA. (E) Immunoblotting analysis of Rad53 phosphorylation from the experiments shown in panels (A, D). (F) Analysis of checkpoint activation following replication stress. Wild type, mrc1-aid, mrc1-aid ctf18-RAA dcc1WH3Δ/pol2-5A cells were arrested in G1, incubated with 0.5 mM IAA final concentration for 1 h and released in medium containing 0.2 M HU and 0.5 mM IAA. Cells samples were collected at the indicated times and analyzed by immunoblotting for Rad53 (left) and Mrc1/mrc1-aid (right). Ponceau staining is shown for loading comparison.