Figure 1. Basal respiration and chemoresponsive instability in Kcna1−/− mice.
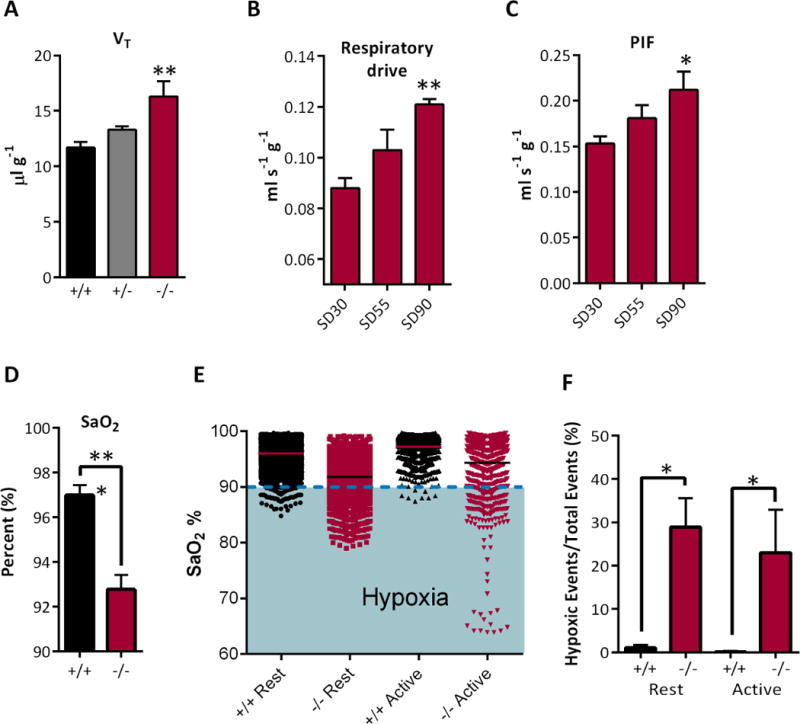
A) Tidal volume (VT) is increased in SD90 Kcna1−/− mice (F (2,14) = 6.9). (B) As Kcna1−/− mice age respiratory drive (VT/Ti: F (2,14) = 8.9) and (C) PIF (F (2,14) = 3.5) are elevated. Significance was determined by two way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, n = 5-7. (D) Pulse oximetry indicates that arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is lower in SD55 Kcna1−/− mice compared to age matched Kcna1+/+ mice (data expressed as mean per animal ± SEM, n = 4 mice). (E) Plotting all SaO2 measurements indicates oxygen desaturation during different behavioral states by ~4% and illustrates frequent excursions into hypoxia when SaO2 < 90%. (F) Quantification of the percentage of measurements with SaO2 < 90%, unpaired Mann-Whitney test; n = 8, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
