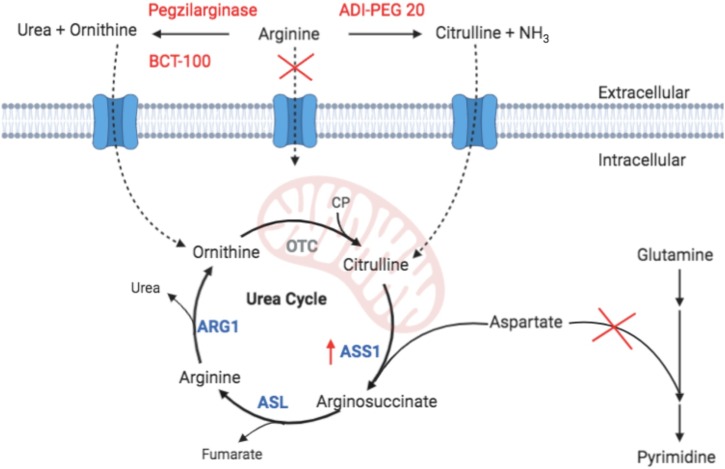
Figure 1.
Extracellular metabolism of arginine by BCT-100, pegzilarginase, and ADI-PEG 20 (pegylated bacterial arginine deiminase) reduces cellular uptake of free arginine, resulting in upregulation of argininosuccinate synthetase 1 (ASS1). Ornithine generated by BCT-100 and pegzilarginase cannot be converted into citrulline outside the liver and intestines as ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) is not expressed (gray); therefore, arginine cannot be synthesized and utilized for viral replication. In contrast, citrulline produced by ADI-PEG 20 is more easily converted to arginine outside the liver since ASS1 and arginosuccinate lyase (ASL) are expressed in most tissues; therefore, viral replication may not be impeded as effectively. A consequence of ASS1 upregulation is that any available citrulline will be rapidly conjugated to aspartate, preventing its utilization in pyrimidine ring synthesis, thereby restricting viral replication of another key building block. ARG1, arginase 1; CP, carbamoyl phosphate.