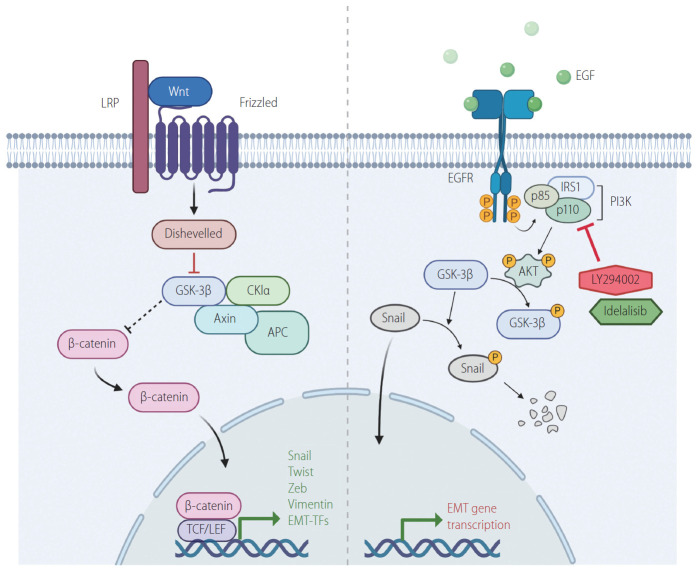
Figure 1.
Regulation of EMT transcription factors by Wnt/GSK3β/β-catenin/Snail and PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/Snail signaling. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT pathways stimulates EMT pathway by suppressing GSK3β, which in turn is inhibited from destabilizing Snail. Suppression of GSK3β also stabilizes β-catenin, which in turn involved in the expression of EMT genes such as vimentin and EMT-TFs. Idelalisib and LY294002 are PI3K inhibitors, which prevent AKT activation. This leads to the release of GSK3 β from PI3K/AKT-mediated suppression. The active GSK3β then phosphorylates Snail, leading to its degradation. LRP, low-density-lipoprotein-related protein; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; TCF, T-cell factor; LEF, lymphoid enhancing factor; EMT-TFs, epithelial-mesenchymal transition-activating transcription factors; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; IRS1, insulin receptor substrate 1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.