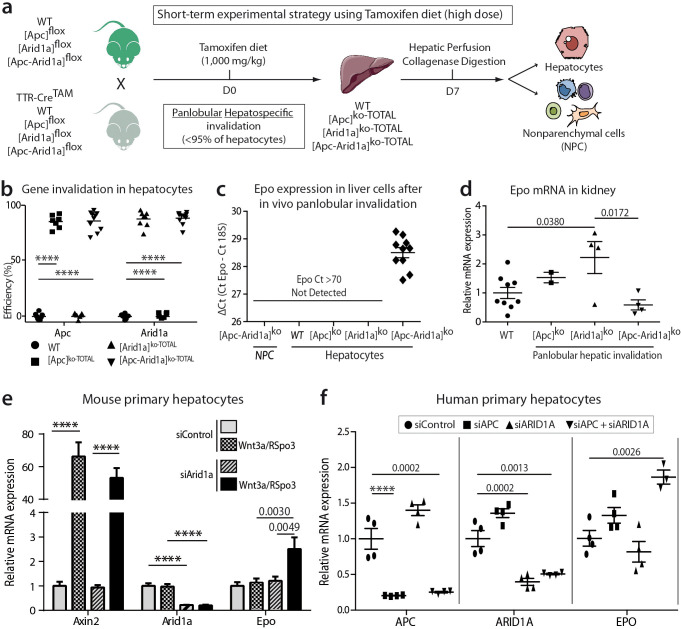
Figure 5. Cell-autonomous Epo expression after Arid1a inactivation and Wnt/β-catenin activation in murine and human hepatocytes.
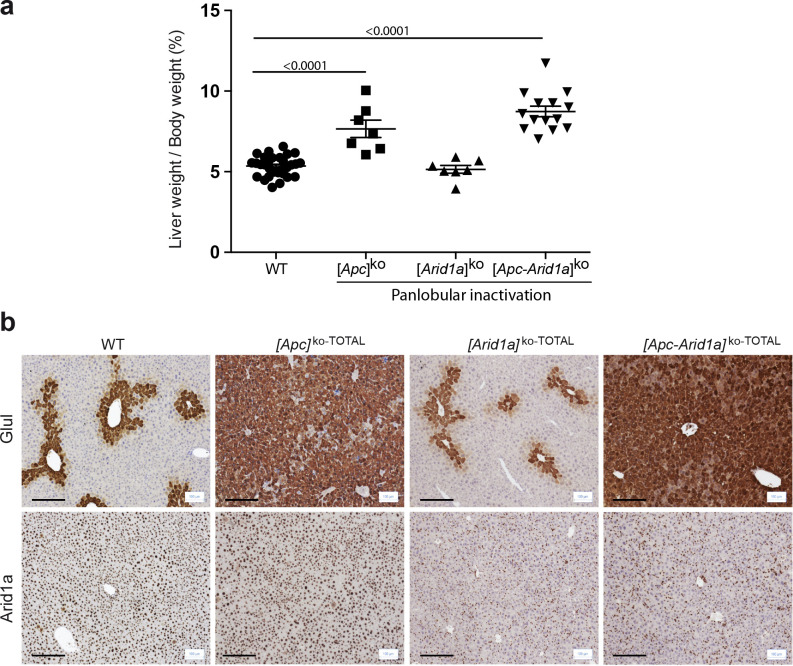
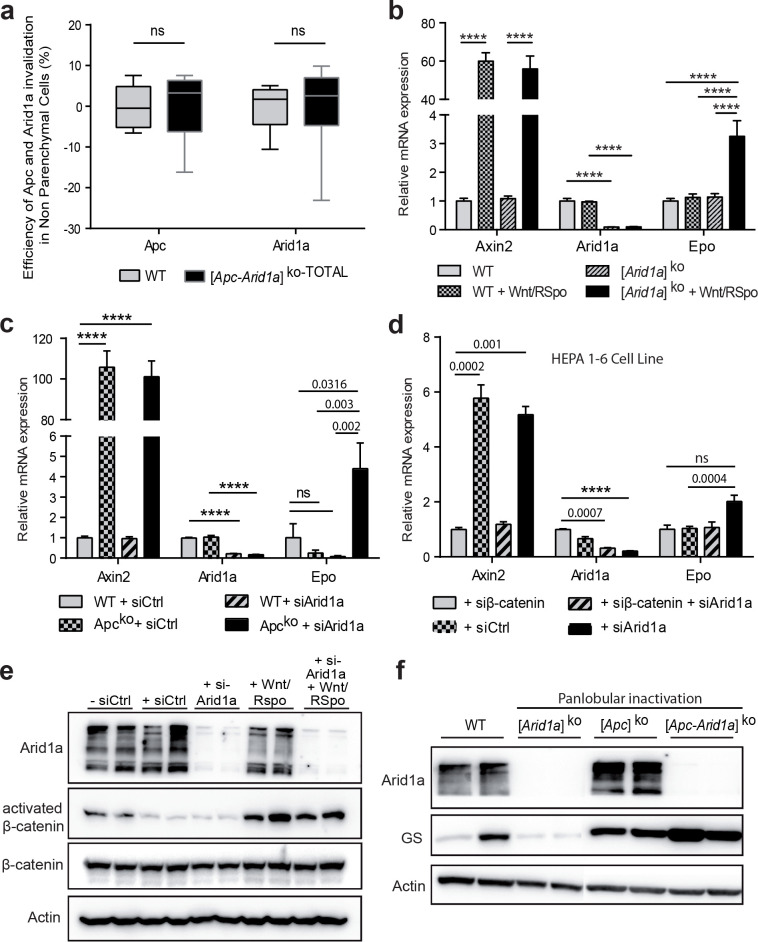
(a) In vivo and ex vivo strategy. WT (n = 8), [Apc]ko-TOTAL (n = 7), [Arid1a]ko-TOTAL (n = 8), and [Apc-Arid1a]ko-TOTAL (n = 10) mice. (b) Inactivation efficiency of Apc and Arid1a genes in isolated hepatocytes. (c,d) RT-qPCR assessment of erythropoietin (Epo) transcription (c) in the hepatocyte and NPC compartments of the livers, (d) in the kidney (1-way ANOVA). (e) In vitro analysis of Axin2, Arid1a (Arid1a floxed-exon detection), and Epo expression by RT-qPCR of mouse hepatocytes after Wnt3a and R-Spondin3 stimulation, and si-Arid1a/si-Control treatments, showing Arid1a knockdown efficiency and Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation, as the mRNA levels of Axin2, a canonical target gene of Wnt signaling, significantly increased (2-way ANOVA). (f) In vitro analysis of Apc, Arid1a, and Epo by RT-qPCR of cryopreserved human hepatocytes after siRNA transfection (one-way ANOVA analysis). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ****p<0.0001. Cell culture data are representative of three independent experiments. Related data are found in Figure 5—figure supplements 1–2, and source data in ‘Figure 5—source data 1; Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1; Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 1’.