Figure 1.
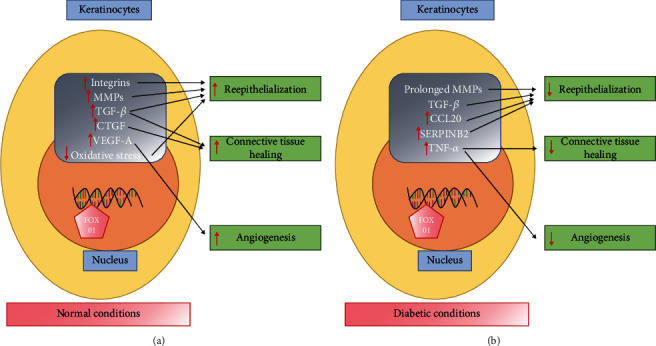
(a) Under normal conditions, FOXO1 promotes reepithelialization through upregulating the expression of integrins, MMPs, TGF-β, and antioxidants. FOXO1 promotes connective tissue healing through induction of the TGF-β and CTGF expression and stimulates angiogenesis via upregulating VEGF-A. (b) In diabetic conditions, FOXO1 exhibits reduced binding to the TGF-β1 promoter to diminish the TGF-β1 expression. However, its interaction with a number of factors that inhibit healing when expressed at high levels is increased including MMP-9, CCL20, IL-36γ, and SERPINB2 which hamper reepithelialization. FOXO1 is induced by high levels of glucose, advanced glycation end products, and TNF that are elevated in diabetic wounds.
