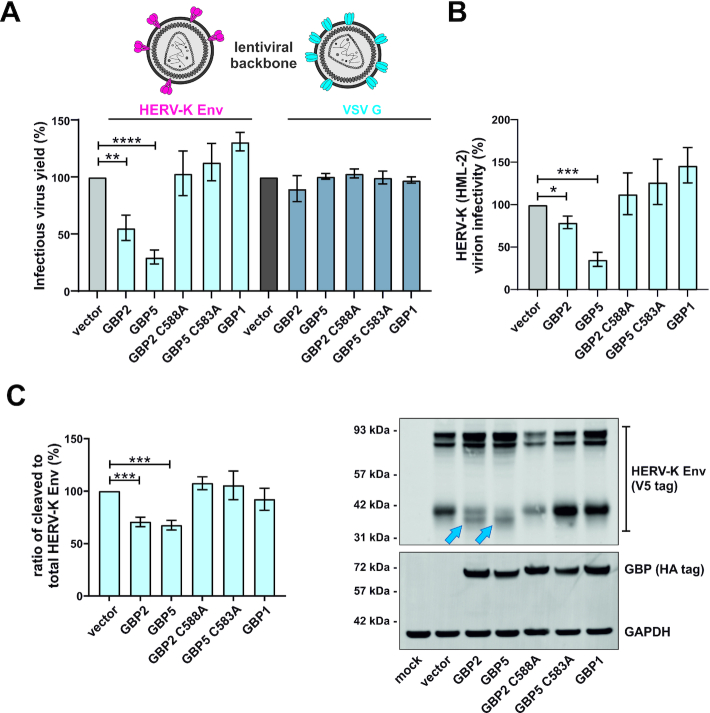
Figure 8.
GBP2 and GBP5 interfere with HERV-K (HML-2) maturation and reduce HERV-K (HML-2) pseudovirion infectivity. (A) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with an env-deficient lentiviral luciferase reporter construct (pSIvec1ΔenvLuc) and expression plasmids for HIV-1 Rev, the indicated GBPs and either HERV-K Env Δ659–699 (left) or VSV G (right). Two days post transfection, cell culture supernatants were harvested, and infectious pseudovirion yield was determined by infecting CRFK cells and quantifying luciferase activity three days later. Mean values of 2–3 independent experiments ± SEM are shown (**P <0.01; **** P <0.0001). A cartoon illustrating HERV-K and VSV pseudoparticles is shown on top. (B) To calculate HERV-K pseudovirion infectivity, total infectious yield of the samples shown in (A) was normalized to the amount of p27 capsid as determined by ELISA. Mean values of 3 independent experiments ± SEM are shown (**P <0.01; **** P <0.0001). (C) HEK293T cells were described in (A). Two days post transfection, cells were harvested and expression of HERV-K Env, GBP and GAPDH was determined by Western blotting. Blue arrows indicate a shift in the electrophoretic mobility of HERV-K Env in the presence of GBP2 and GBP5. Cleavage efficiency of HERV-K Env was quantified by determining the ratio of cleaved to total Env. The quantification of 4 independent blots ± SEM is shown on the left (** P <0.01; *** P <0.0001; **** P <0.0001). One representative Western blot is shown on the right.