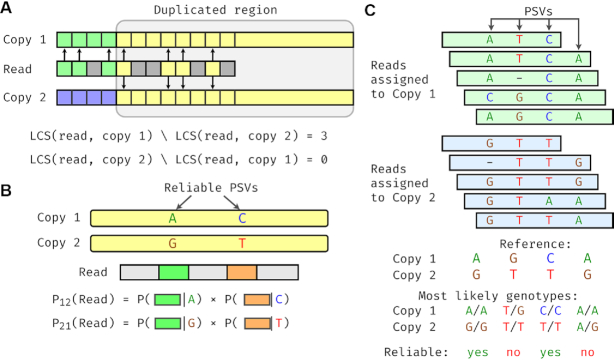
Figure 1.
Overview of the DuploMap method. (A) Filtering alignment locations using LCS of k-mers. A read partially overlaps a segmental duplication and has two possible alignment locations (copy 1 and copy 2). The read and its possible locations are divided into k-mers that are shown with different colors. Arrows depict k-mers in the LCS between the read and the two copies. In the duplicated region, the read shares four k-mers with ‘copy 1’ that are also shared with ‘copy 2’. Outside the duplicated region, the read shares three k-mers (shown in green) with the k-mers of ‘copy 1’, but not with the k-mers of ‘copy 2’. (B) Calculation of read-location probabilities using PSVs. The read intersects two reliable PSVs that distinguish the two alignment locations. The probability of each location being correct (relative to the other location) is calculated using the local realignment probabilities between the read and the PSVs. (C) Identifying reliable PSVs using assigned reads. Five reads are mapped to ‘copy 1’ and five reads are mapped to ‘copy 2’ with high mapping quality. The genotype likelihoods for each PSV are calculated using these reads. Only two of the four PSVs have the reference genotype as the most likely genotype for both locations of each PSV and are considered reliable.