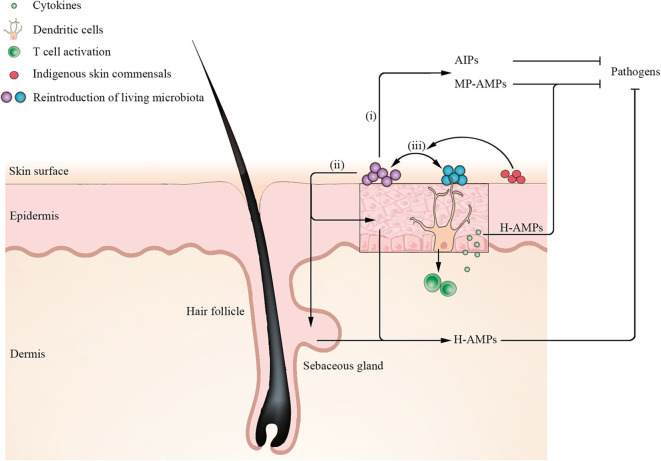
Figure 4.
Mechanisms for establishment and restoration of cutaneous homeostasis by reintroduction of living microbiota. Application of a single of microbiota such as S. hominis secretes microbiota-produced antimicrobial peptides (MP-AMPs) or other metabolites [such as autoinducing peptides (AIPs)] to inhibit pathogen S. aureus. Moreover, reintroduction of living microbiota induces keratinocytes and sebocytes to secrete human AMPs (H-AMPs) to directly inhibit pathogens. Notably, dendritic cells (DCs) extend their dendrites into the stratum corneum to acquire microbial antigens and active T cells to release cytokines. Keratinocytes-produced H-AMPs LL-37 induced by cytokines synergize with MP-MAPs (such as S. epidermidis lantibiotics), which can kill S. aureus more effectively. In addition, reintroduction of a cocktail of microbiota has a synergistic effect on ameliorating the ecology of skin microbial communities. When certain indigenous skin commensals are rich in recipient skin, reintroduction of a cocktail of microbiota has a higher engraftment.