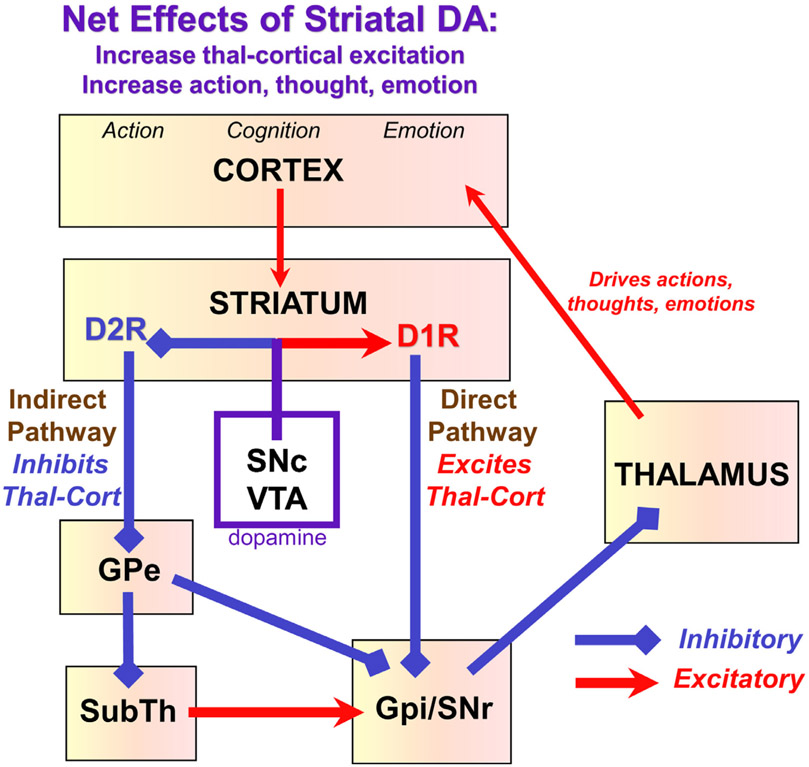
FIGURE 3.
Dopamine effects on basal ganglia circuitry. The basal ganglia have parallel circuits for the control of movement, cognition, and emotion. The basal ganglia regulate the output of the thalamus, and its ability to excite the cortex. There are two major pathways emanating from the striatum: a Direct pathway that overall excites thalamocortical projections (by inhibiting the inhibitory effects of Gpi/SNr on thalamus), and an Indirect pathway that overall inhibits thalamocortical projections (by a still more complex series of connections). Dopamine facilitates movements, thoughts, and emotions by exciting the Direct pathway via D1R, and inhibiting the Indirect pathway via D2R. DA: dopamine; Thal-Cort: thalamo-cortical; GPe: globus pallidus external segment, GPi: globus pallidus internal segment; SubTh: subthalamic nucleus; SNc: substantia nigra pars compacta; SNr: substantia nigra pars reticulate; VTA: ventral tegmental area.