Figure 4. Vision and pigmentation genes localized to previously identified QTL providing novel candidate genes.
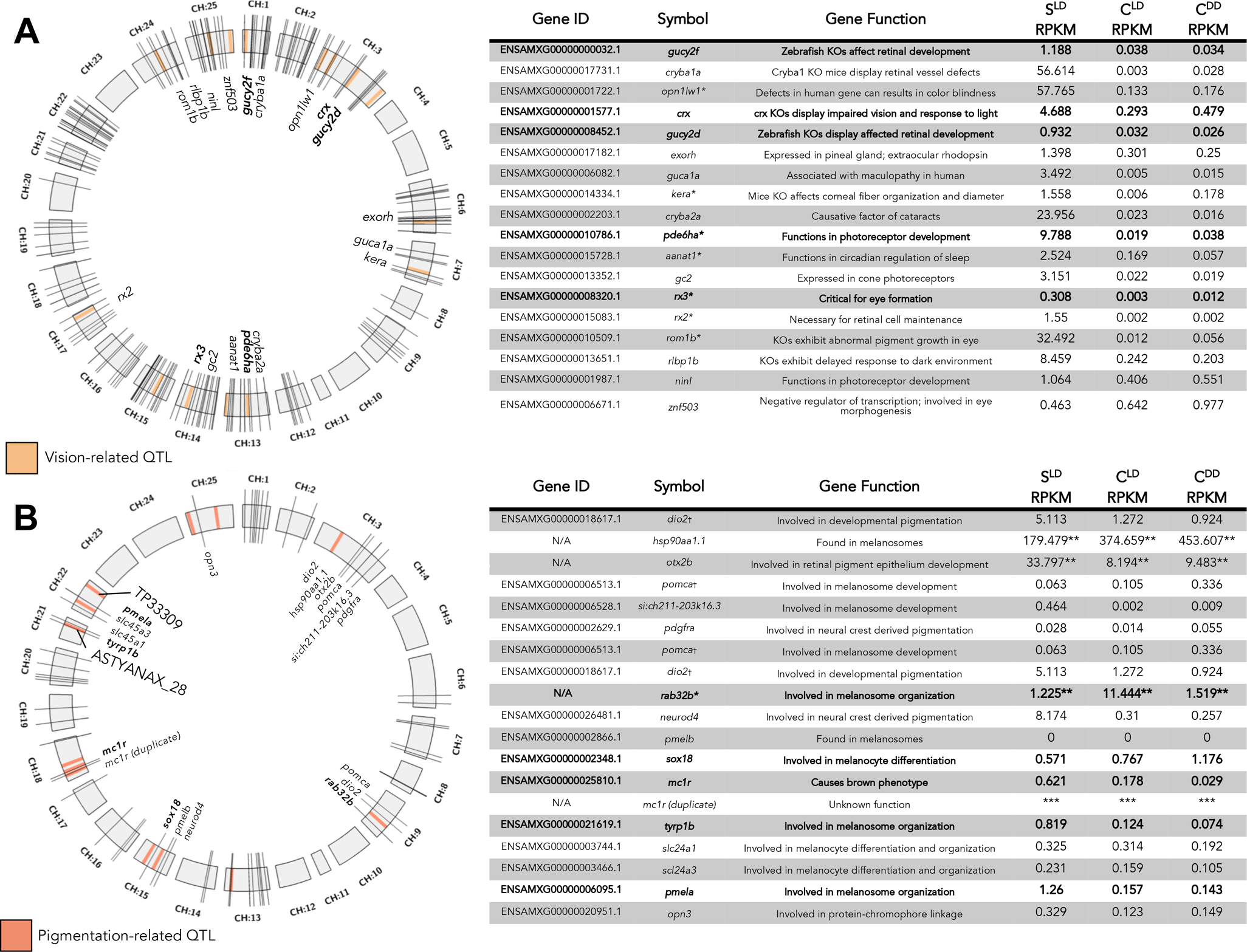
The distribution of vision-related (A) and pigmentation-related (B) QTL (light orange or light pink boxes) across the 25 chromosomes of the draft Astyanax genome (gray boxes, CH:1–25). Gene identity and function are represented in the tables to the right. Values are given in RPKM (normalized expression). Some genes fall remarkably close to QTL (represented as bold hash marks and text) and demonstrate relevant alterations in development when function is disrupted in other systems. * indicates gene name was derived from Danio rerio based on sequence similarity. ** indicates RPKM was obtained via RNA-seq alignment to Astyanax NCBI draft genome by chromosome, and cannot be directly compared to other values, although intra-gene comparisons of expression based on morphotype and lighting condition are valid. † indicates an A. mexicanus gene that aligns to the same protein in D. rerio as another A. mexicanus gene by BLAST. *** is used in place of expression values for the duplicate mc1r gene due to incomplete functional and coding information for this copy number variant.
