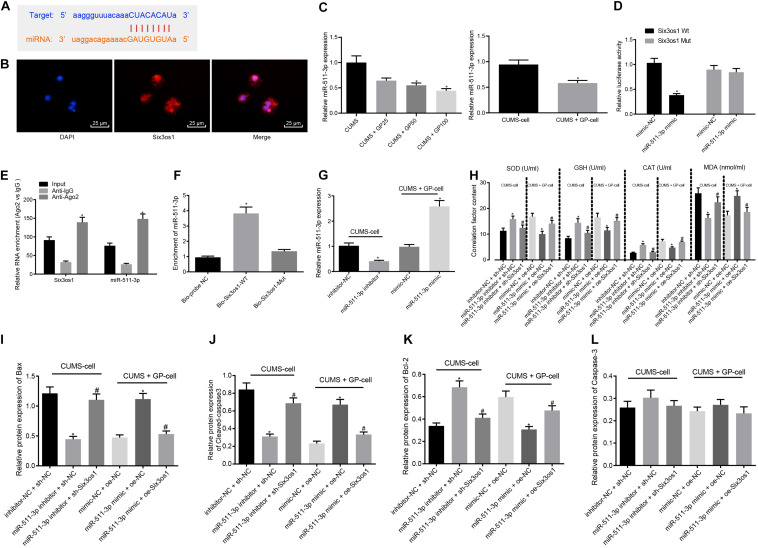
FIGURE 3.
Six3os1 alleviates oxidative stress in CUMS-induced neurons through inhibiting miR-511-3p. (A) The targeting relationship between Six3os1 and miR-511-3p predicted by StarBase website. (B) The subcellular localization of Six3os1. (C) miR-511-3p expression in mice (n = 15) and neurons after CUMS and GP treatment detected by RT-qPCR. (D) The targeting relationship between Six3os1 and miR-511-3p verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. (E) The targeting relationship between Six3os1 and miR-511-3p determined by RIP assay. (F) The targeting relationship between Six3os1 and miR-511-3p determined by RNA pull down. (G) miR-511-3p expression in neurons after treatment of miR-511-3p inhibitor and miR-511-3p mimic detected by RT-qPCR. (H) SOD, GSH, CAT, and MDA contents in neurons after alteration of Six3os1 and miR-511-3p examined by ELISA. (I–L) Quantitation of Bax (I), Cleaved caspase-3 (J), Bcl-2 (K), and caspase-3 (L) protein expression normalized to GAPDH in cells after alteration of Six3os1 and miR-511-3p detected by Western blot analysis. The measurement data were presented as mean ± standard deviation. Data between two groups were compared by independent sample t-test, and data among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Cell experiments were repeated three times. ∗p < 0.05 vs. CUMS-induced mice, CUMS-induced neurons, inhibitor-NC + sh-NC, mimic-NC + oe-NC, oe-NC or sh-NC. #p < 0.05 vs. miR-511-3p inhibitor + sh-NC or miR-511-3p mimic + oe-NC.