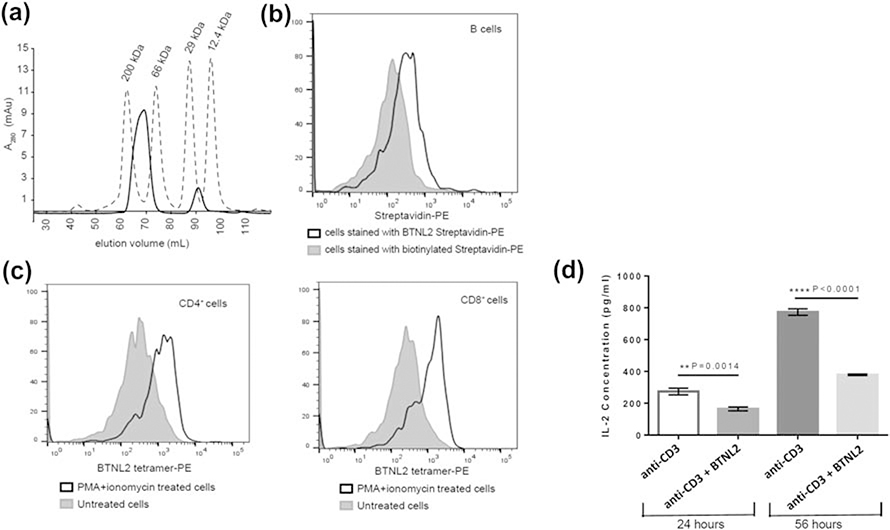
Figure 2: BTNL2 IgV domain binds to its putative receptor expressed on naïve B cells and in vitro activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
A. Biotinylated BTNL2 was tetramerized using streptavidin, which elutes at 69.2 ml (solid line) in HiLoad™ 16/600 Superdex™ 200 pg SEC column. Molecular weight standards are also indicated B. BTNL2 was tetramerized with PE-conjugated streptavidin. Binding of BTNL2 tetramer was analyzed by gating on CD19+ B cells using biotinylated streptavidin-PE as a control to account for any non-specific binding of the tetramer. C. Untreated as well as PMA/ionomycin activated splenocytes were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated anti-CD3, and anti CD4 (left panel) or anti-CD8 (right panel) antibodies followed by incubation with PE-conjugated BTNL2 tetramer. The solid gray histogram represents BTNL2 tetramer binding to untreated cells, while the white histogram represents binding of the tetramer to PMA/ionomycin treated cells. D. Sorted CD4+ T cells were stimulated with plate-bound anti CD3 antibody with or without immobilized BTNL2 IgV monomer for 24 hours (p value = 0.0014) and 56 hours (p value ˂ 0.0001). The supernatant were collected and analyzed for IL-2 secretion. Data represents mean with SEM of 3 biological replicates for each set. p value was calculated using unpaired T test.