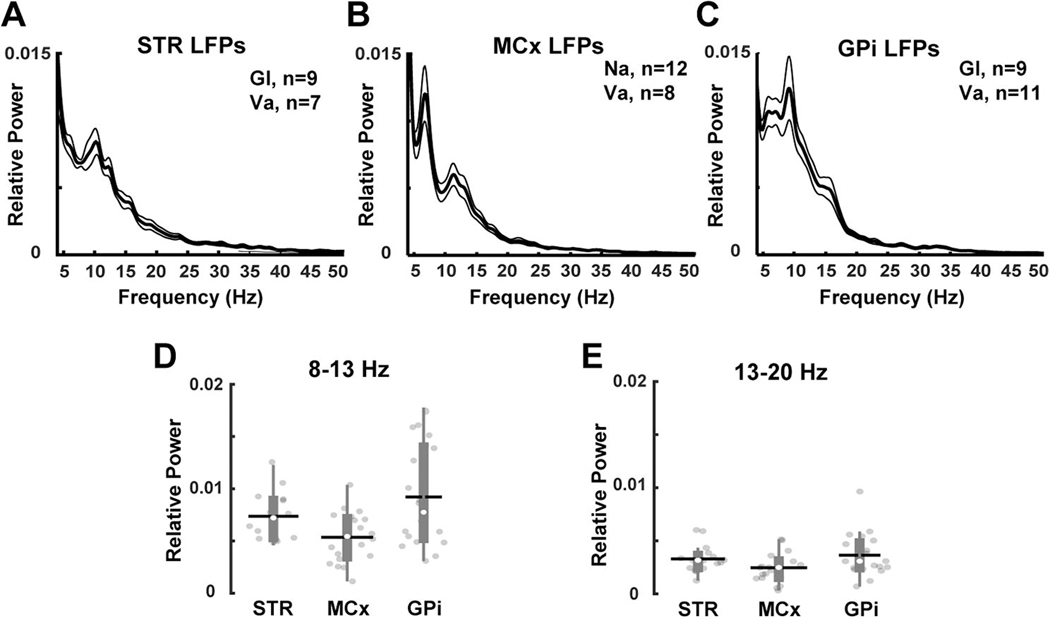
Figure 2. LFPs recorded from motor cortex and basal ganglia nuclei.
(A) Striatal (Gl, n=9; Va, n=7 recordings), (B) motor cortical (Na, n=12; Va, n=8 recordings), and (C) internal pallidal (Gl, n=9; Va, n=8 recordings) oscillations recorded in parkinsonian NHPs. (D-E) Comparison of the relative power of 8–13 Hz and 13–20 Hz frequency bands in each of the studied regions. The relative powers of LFPs at 8–13 Hz and 13–20 Hz were similar across the motor cortex, the striatum and the GPi. Thick and thin lines represent mean and standard error of mean, respectively. STR= striatum; MCx= motor cortex; GPi= globus pallidus internus. The black horizontal lines and white circles in the box plots represent the mean and median values, respectively.