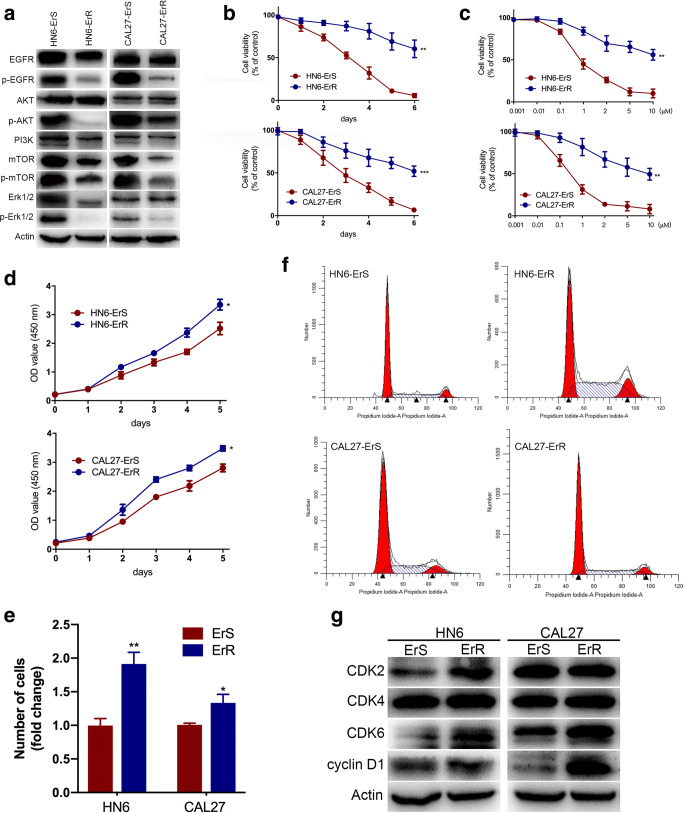
Fig. 1.
Erlotinib inhibited canonical EGFR signaling and increased proliferation in resistant cells. a Total and phosphorylation of EGFR, AKT, mTOR and Erk1/2 were analyzed by Western blot. Phosphorylation of EGFR, AKT, mTOR and Erk1/2 was markedly decreased in both HN6 and CAL27 resistant cells. b Cell viability was tested in sensitive and resistant HN6 and CAL27 cells. c The half-maximal inhibitory concentration value of erlotinib was detected for sensitive and resistant cells by cell viability assay. d CCK-8 assays showed that erlotinib-resistant cells exhibited higher tumorigenicity than the parental cells. e colony-formation assays displayed enhanced proliferative abilities in HN6-ErR and CAL27-ErR cells after two-week incubation. f Cell-cycle analysis was performed by flow cytometry in sensitive and insensitive cells. ErR cells presented a significantly lower percentage in the G1 phase and higher percent of cells in the S and G2 phase than ErS cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001