Figure 4. KDM6A, UTY, KDM5C and KDM5D: structure and function.
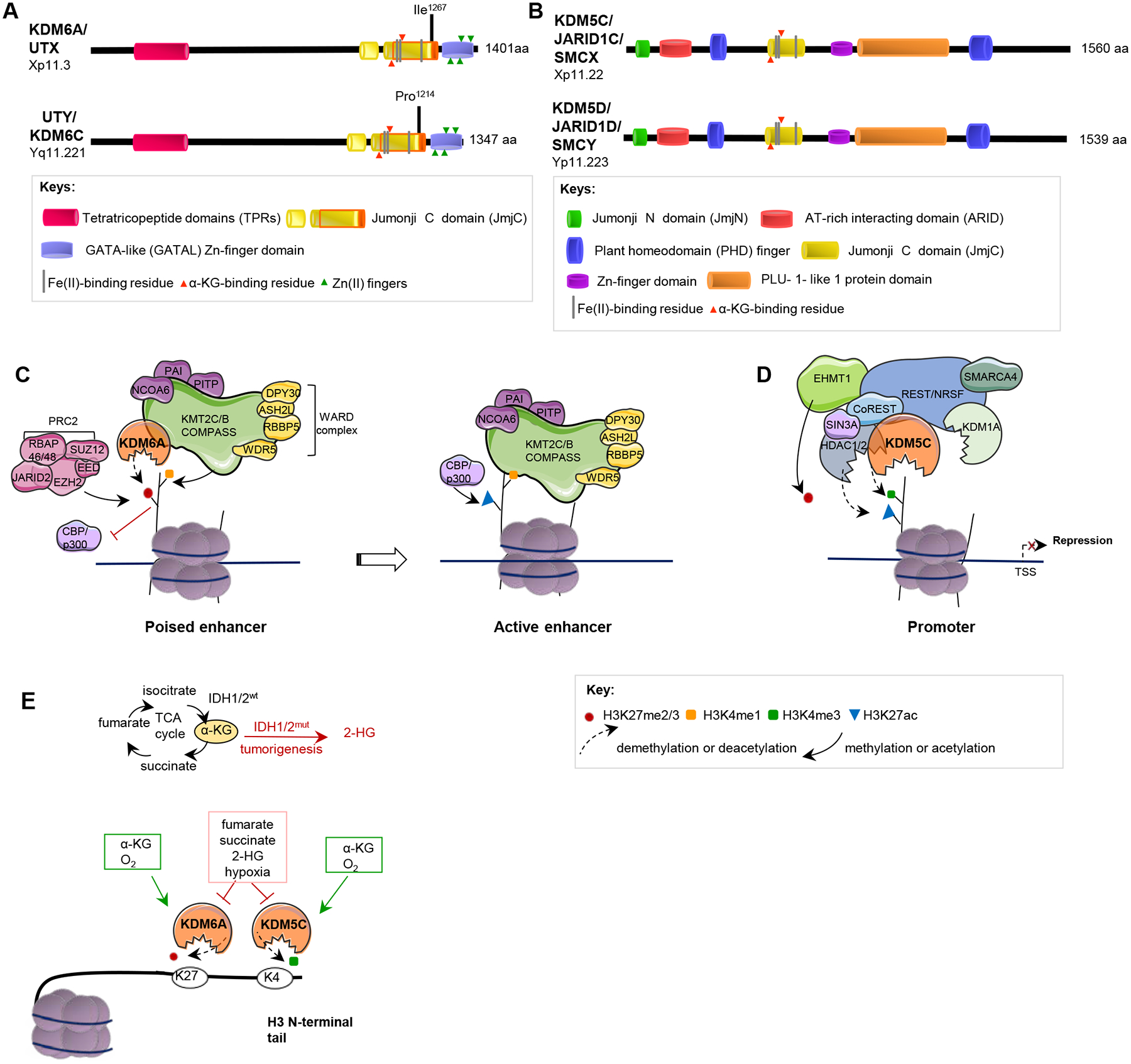
A, B. Domain structures of KDM6A and UTY (A), and for KDM5C and KDM5D (B) are indicated. The core catalytic domain, JmjC, demethylates histones by an oxidative mechanism requiring Fe(II) and alpha-ketoglutarate (α−KG) as cofactors; JmjN, in JARID proteins, interacts with JmjC, inducing a conformational change that promotes enzymatic activity. ARID and PLU-1 are DNA binding domains. TPR domains mediate interactions with other proteins including the KMT2C-KMT2B complex (49). The Zn-fingers mediate histone tail recognition; the PHD domain binds H3K9me3, coordinating H3K4 demethylation. Note, each protein family contains additional paralogous members (KDM5A (Chr 12), KDM5B (Chr 1) and KDM6B (Chr 17)), which have related but not equivalent function. See legend to Supp Fig 1 for extended comment on placement of motif boundaries. C. Through its activity as a histone H3K27me2/3 demethylase, KDM6A opposes activity of the repressive PRC2 complex, converting poised enhancers to transcriptionally active enhancers. KDM6A is also a component of the KMT2C-KMT2B COMPASS-like complex. As part of this complex, KDM6A contributes to protein recruitment at enhancers and cooperates with other complex components, including the lysine methyltransferases (KMTs) KMT2C and KMT2B, which monomethylate H3K4 (H3K4me1) and the histone acetyltransferases (HATs) p300 and CBP, which acetylate H3K27. These actions result in enhancer activation (118). Loss of KDM6A activates PRC2-regulated transcription repression, similar to EZH2 gain-of-function mutations, and sensitizes tumors to EZH2 inhibitors (78). KDM6A mutations damaging the TPR domain disrupt interaction with KMT2C-KMT2B complexes (49). D. KDM5C associates with Co-REST, Sin3a and other proteins to demethylate H3K4me3 at specific promoters, causing gene repression. E. Metabolic factors influencing the activity of KDM6A, UTY, KDM5C and KDM5D. Mutations in fumarate hydratase (FH), succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) or isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH1, IDH2) affecting pools of the metabolites fumarate, succinate, or 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), or hypoxia, repress KDM6A and KDM5C activity (119,120).
