Figure 5.
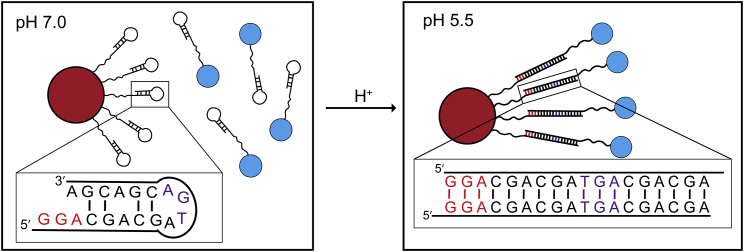
Potential use of (CGA)6 and variants in DNA nanotechnology applications in which pH changes could localize particles together. At pH 7.0, d(CGA) forms hairpin structures, preventing duplex formation, and particles remain separate. At pH 5.5, parallel-stranded duplexes can form and localize particles of interest together. d(TGA) and d(GGA) triplets can be used to ensure desired registration and length of the linking duplex. Linker stretches solely comprised of d(CGA) triplets could be used, but distance between particles of interest could vary. To see this figure in color, go online.