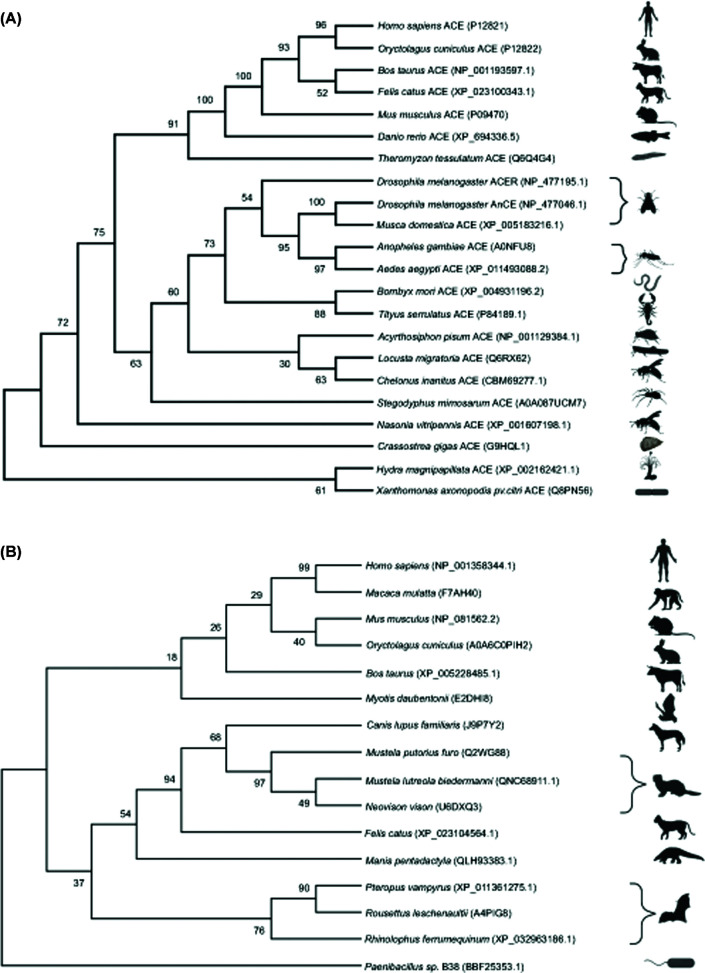
Figure 1. ACE and ACE2 inferred phylogeny of selected representative species.
Protein sequences were aligned and analysed using Maximum Likelihood (ML) with 1000 replicates in MEGA X. Accession numbers were included with each taxon and branch supports are shown at each node indicating percentage agreement of node position amongst bootstrap replicates. Branch supports below 70% are not well supported. Animal icons were obtained through BioRender. Only metallopeptidase ACE homologues were included in the analysis and only incomplete sequences for Locusta migratoria, Chelonus inanitus and Myotis daubentonii were available at the time of sequence acquisition. (A) Invertebrate ACE and ACE-like peptides identified in venom are clustered together and included in the representative ACE phylogeny. Moreover, vertebrate mammalian ACE has greater evolutionary support of a close relationship than seen in the invertebrate species. (B) ACE2 phylogeny includes sequences of pangolin and bat species indicated as potential hosts for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. In some nodes, ACE2 may be too divergent due to missing data, gene flow or recombination for higher branch support values.