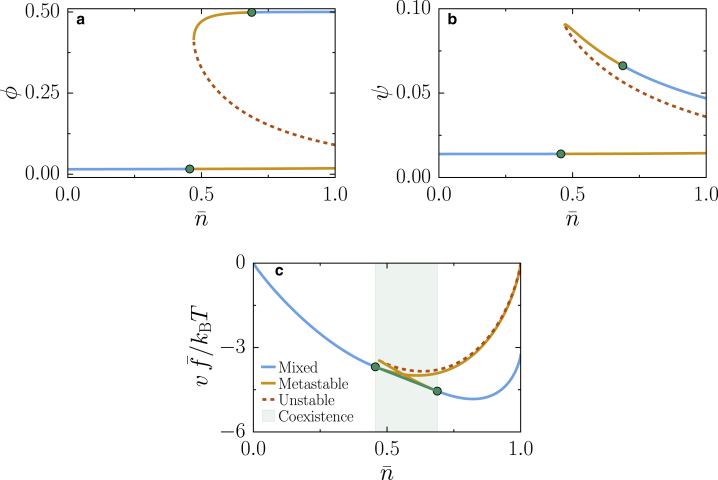
Figure 1.
Chemical equilibrium conditions and free-energy density at chemical equilibrium. Multiple solutions are found for ϕ (a) and ψ (b) as a function of the total macromolecule volume fraction , enabling the system to exhibit phase separation between different branches of the chemical equilibrium. The blue solid lines correspond to equilibrium concentrations at which the system remains homogeneous, the orange solid lines represent solutions to the chemical equilibrium relations that are metastable states, and the dotted red line shows the unstable states. (c) Maxwell construction for the dimensionless free-energy density /kBT is shown as a function of the total macromolecule volume fraction; the green line describes the region of macromolecule volume fraction where the system split into two phases, with different compositions given by the green circles. Parameters χe/kBT = −3, χn = 0, pI − pH = 0.2, hϕ/kBT = −10, and ε = 0.1 apply to all panels. To see this figure in color, go online.