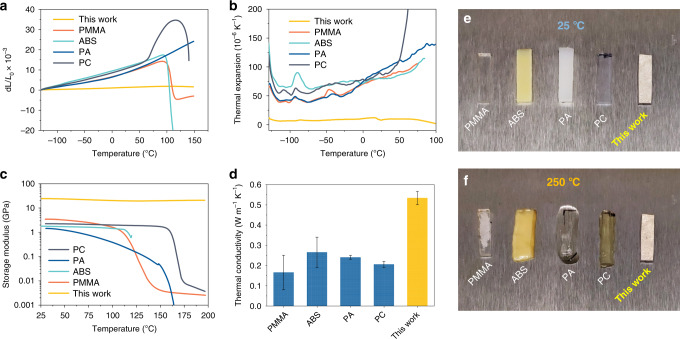
Fig. 4. Comparison of thermal properties of all-natural bioinspired structural material with widely used plastics.
a Comparison of thermal expansion of the all-natural bioinspired structural material with widely used petroleum-based plastics. b Comparison of coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the all-natural bioinspired structural material with widely used petroleum-based plastics. c Comparison of storage modulus of the all-natural bioinspired structural material with widely used petroleum-based plastics. d Comparison of thermal conductivity of the all-natural bioinspired structural material with widely used petroleum-based plastics31. Error bars represent standard deviation. e, f Thermal stability experiment. Comparison of the all-natural bioinspired structural material with widely used petroleum-based plastics at e 25 °C and f 250 °C. Compared to 25 °C, petroleum-based plastics have already fully softened at 250 °C, while all-natural bioinspired structural material still shows no visible change. PMMA polymethyl methacrylate, ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, PA polyamide, PC polycarbonate.