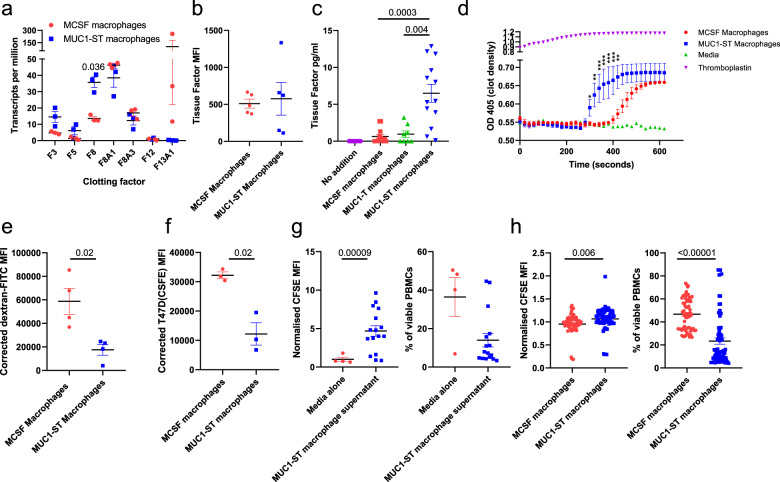
Fig. 5. MUC1-ST macrophages induce clotting, are inefficient at phagocytosis and inhibit T-cell proliferation and viability.
a Clotting factor transcript expression levels in MUC1-ST (n = 3 biologically independent samples) and MCSF macrophages (n = 3 biologically independent samples). b Cell surface bound (n = 5 biologically independent samples) and c secreted levels of tissue factor (n = 13 biologically independent samples); excluding MUC1-T where n = 8 biologically independent samples. d Plasma clotting in the presence of indicated factors or supernatants at indicated time points. e, f Bar charts showing corrected (37 °C MFI minus 4 °C MFI) of e dextran-FITC uptake (n = 4 biologically independent samples) and f uptake of CFSE-labelled T47D tumour cells (n = 3 biologically independent samples) by M-CSF macrophages and MUC1-ST macrophages after 4 h incubation. g Pooled data showing proliferation (relative CFSE expression) and viability of CD3 stimulated PBMCs in the presence of media alone (n = 4 biologically independent samples) or MUC1-ST macrophage supernatant (n = 16 biologically independent samples). h Mixed leucocyte reaction showing proliferation and viability of PBMCs when co-cultured with MCSF macrophages or MUC1-ST macrophages at a 5:1 ratio for 4 days (n = 16 biologically independent samples, in quadruplet). Standard error of the mean shown and paired t test used for statistical analysis, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.