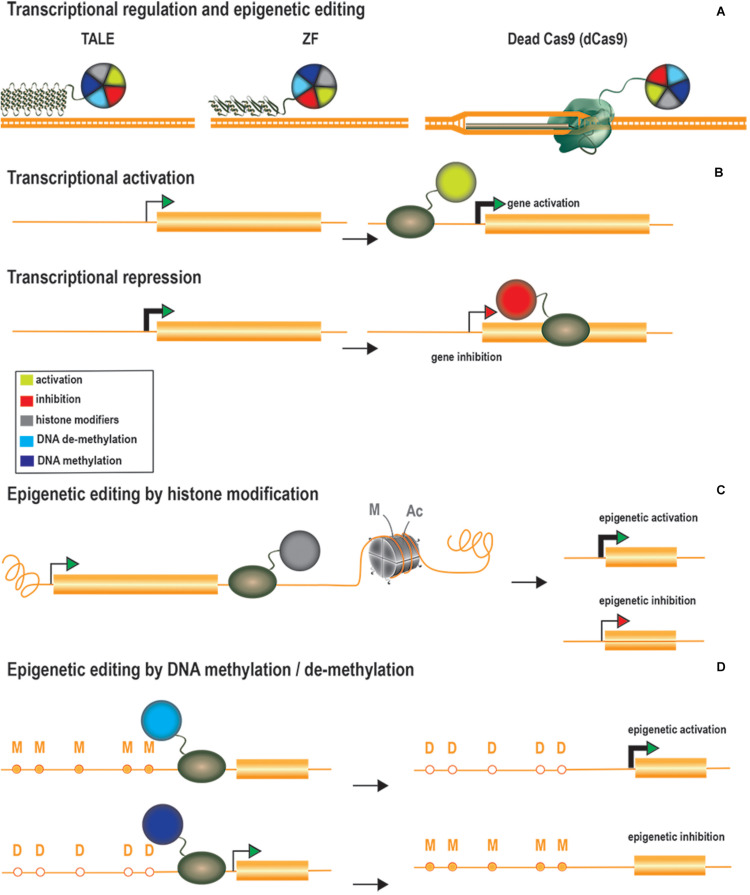
FIGURE 3.
Transcriptional regulators, epigenetic modifiers, and therapeutic approaches. (A) Gene expression regulation tools are generated by fusing TALEs, ZFs or dCas proteins to scaffold transcriptional modulators or to epigenetic modifiers (B) Therapeutic approaches by transcriptional regulation. Transcriptional activation or repression is explored to upregulate therapeutic genes or to downregulate deleterious genes, respectively. Transcriptional activators are targeted at the promoter region whereas transcriptional repressors are usually targeted downstream to the transcription starting site to further block the RNA polymerase activity. (C) Therapeutic approaches through histone modification. Histone (de)acetylases and (de)methylases are the most common employed enzymes to modify histone marks and the epigenetic activation or inhibition effect of such modifications is frequently context-specific. (D) Therapeutic approaches by editing the DNA methylation state. Epigenetic editors based on DNA demethylases are used to activate gene expression whereas the ones based on DNA methylases result in gene expression inhibition.