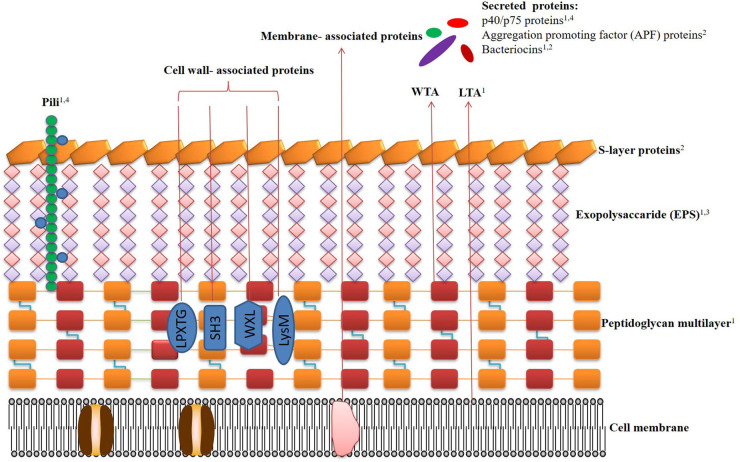
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the cell surface architecture of Lactobacilli, the bilipidic cell membrane (CM) with embedded proteins is covered by a multilayered peptidoglycan (PG) shell decorated with lipoteichoic acids (LTA), wall teichoic acids (WTA), pili, proteins, and lipoproteins. Exopolysaccharides (EPS) form a thick covering closely associated with PG and are surrounded by an outer envelope of S-layer proteins. The beneficial effects of the paraprobiotics and postbiotics are denoted by numbers. (1) immunomodulatory effects; (2) antagonistic effects against pathogens; (3) anti-tumor effects; (4) preservation of intestinal barrier. Related references are as follows. Pili: immunomodulatory effects (46–48), preservation of intestinal barrier (46, 72). Protein p40/p75: immunomodulatory effects (74), preservation of intestinal barrier (17, 75–78). Aggregation promoting factor (APF) proteins: antagonistic effects against pathogens (79–83). Bacteriocins: immunomodulatory effects (9, 84–87), antagonistic effects against pathogens (88–91). LTA: immunomodulatory effects (7, 92, 93). Peptidoglycan: immunomodulatory effects (39, 94, 95). S-layers proteins: antagonistic effects against pathogens (96–98). Exopolysaccharides (EPS): immunomodulatory effects (99–102), anti-tumor effects (75, 103–106).