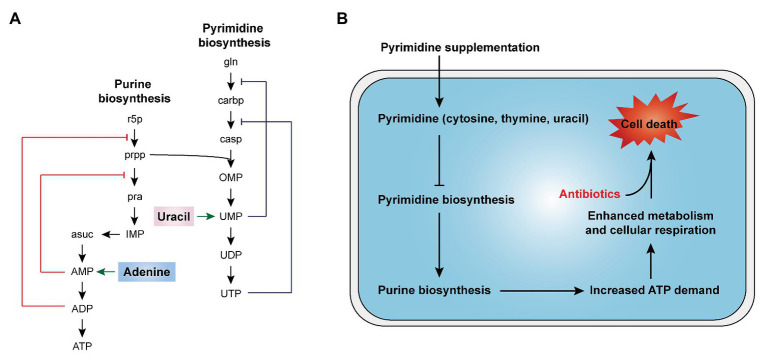
Figure 5.
Nucleotides supplementation activates bacterial metabolism (Yang et al., 2019). (A) Purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis pathways and feedback inhibition by products. (B) The addition of exogenous pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine, and uracil) displays a feedback inhibition on the pyrimidine biosynthesis and triggers purine biosynthesis, thus increasing ATP demand, which drives increased activity through central carbon metabolism and cellular respiration, ultimately restoring the killing of antibiotics against tolerant bacteria.