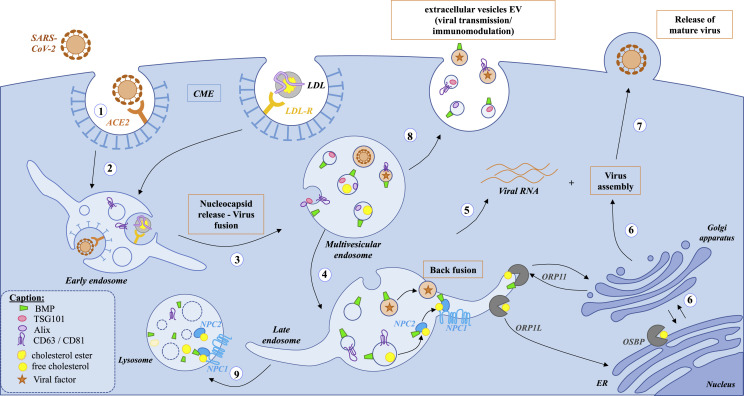
Fig. 2.
Schema of the endocytic pathway involving the endolysosomal lipid BMP and putative relation to SARS-CoV-2 infection steps. (1) binding step: SARS-CoV-2 binds through its spike S protein to its receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) located in lipid rafts on the host cell plasma membrane. (2) internalization step: then SARS-CoV-2 is internalized by clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) and undergoes intracellular trafficking through the endocytic pathway: (3) from early endosome and multivesicular endosome to (4) late endosome/lysosome. The same endocytic route is used by low density lipoproteins (LDL) for cholesterol entry into mammalian cells after binding to the LDL receptor. The virus uncoating and fusion step are strongly dependent of the acidic pH of the endolysosomal compartment enriched in BMP (green conical cylinder): enzymatic cleavage by cathepsin L is crucial for subsequent release of the viral RNA genome (5) into the host cytosol. (6) Newly made viral S protein and other membrane proteins enter the secretory pathway via the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) whereas viral RNA genome and nucleocapsid protein are assembled to form the previral particles into the lumen of the ERGIC (ER-Golgi intermediate compartment). (7) Then, matured viruses are released via transport from the trans-Golgi (TGN) network to the cell surface. (8) Virus factors can also hijack the extracellular vesicle EV secretory pathway to exit infected cells [48]. Recently, BMP (green conical cylinder) was considered as a new lipid signature of endosome-derived EVs characterized by the EV protein markers ESCRT protein TSG101, associated protein Alix, and the tetraspanins CD63 and CD81 [49,50]. The cholesterol transfer between NPC2 and membrane vesicles including between inner membranes of the LE/Lys compartment is favored by BMP [51]. This occurs through the direct interaction of BMP with a domain of NPC2 [52]. This region is also involved in the interaction between the soluble intraendolysosomal NPC2 and the transmembrane protein NPC1 in the limiting membrane of the LE/Lys. This highlights the importance of BMP in NPC2-dependent cholesterol binding at inner membranes of LE/Lys and in NPC2-dependent cholesterol transfer to the N-terminal domain of NPC1. NPC1 has been proposed to be involved in infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 [25]. ORP1L as well as OSBP are required at the replication organelle for viral infection by regulating cholesterol homeostasis [53,54]. We can speculate that ORP11, by interacting with both BMP and cholesterol into late endosome, would be implicated in virus infection.