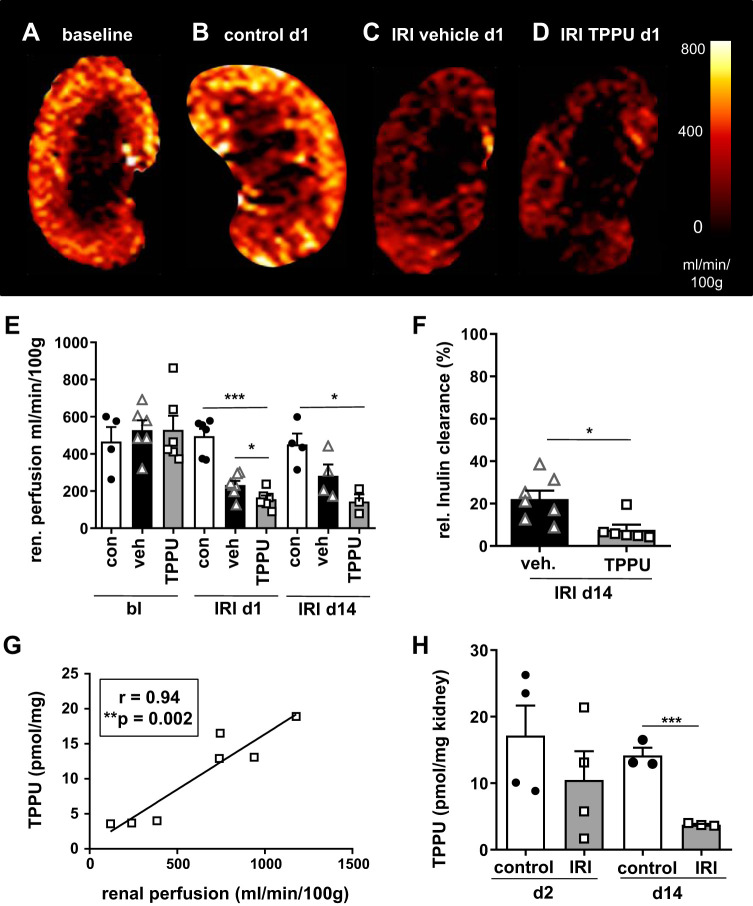
Fig. 4.
1-Trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea (TPPU) aggravated renal perfusion impairment after ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). A−D: renal perfusion was measured by arterial spin labeling. The contralateral kidney at day 1 (d1) served as the control (con; B). Renal perfusion was significantly impaired at day 1 and also at day 14 (d14) after IRI. E: renal perfusion impairment was more profound after TPPU treatment. F: renal function was measured by inulin clearance after contralateral nephrectomy and was poor in vehicle (veh)-treated mice and even worse after blood pressure normalization by TPPU (relative inulin clearance was calculated as a proportion of normal). H and G: TPPU concentration in the renal tissue was lower in IRI kidneys compared with contralateral control kidneys (H) and low renal perfusion correlated with low tissue levels of TPPU (G). bl, baseline; d2, day 2. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.