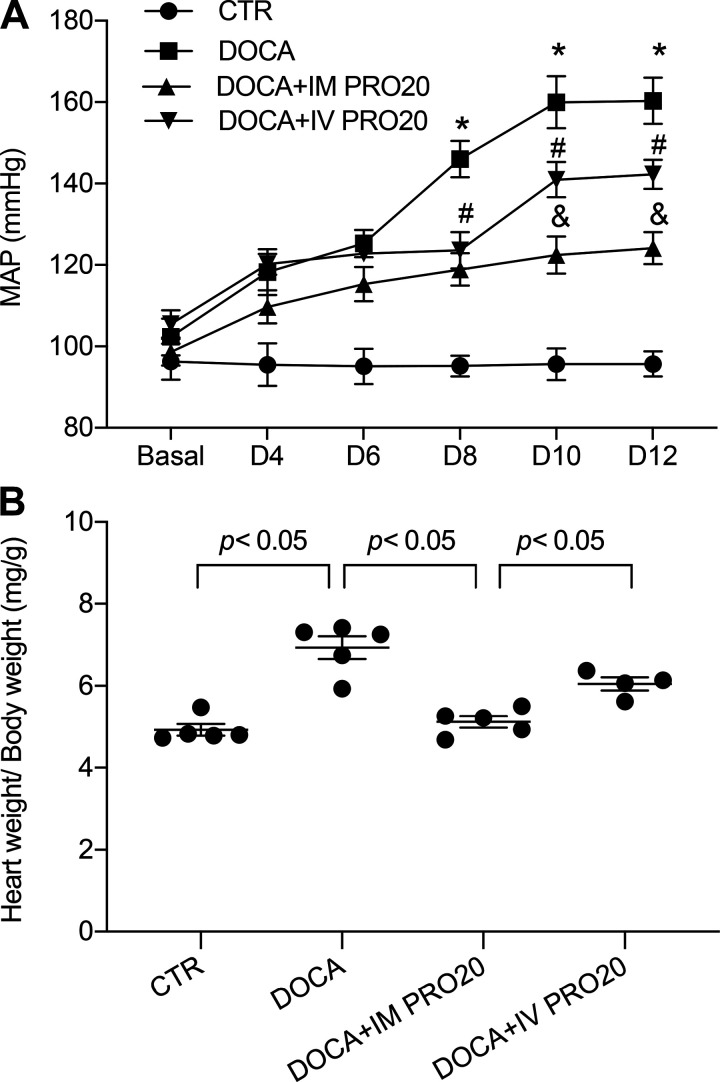
Fig. 3.
Effect of intramedullary (pro)renin receptor inhibition on DOCA-salt hypertension in rats. Uninephrectomized Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into the following four groups: 1) control (CTR), 2) DOCA-salt (DOCA), 3) DOCA + intramedullary PRO20 infusion (IM PRO20), and 4) DOCA + intravenous PRO20 infusion (IV PRO20). The DOCA-salt protocol consisted of subcutaneous implantation of a 50-mg DOCA pellet in combination with 0.9% NaCl as drinking fluid. IM PRO20 (PRO20 at 120 µg·kg−1·day−1) was performed via a catheter chronically implanted in the renal medulla. To control the spillover, IV PRO (PRO20 at 120 µg·kg−1·day−1) was performed via catheterization of the jugular vein. Telemetry was performed to monitor mean arterial pressure (MAP), and it was turned on 4 h/day from 5:00 PM to 9:00 PM. A: radiotelemetry monitoring of MAP. *P < 0.05 vs. CTR; #P < 0.05 vs. DOCA alone; &P < 0.05 vs. IV PRO20. B: heart weight/body weight. n = 5 animals/group. For A, statistical significance was determined using two-way ANOVA with repeated measurements. For B, one-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni test for multiple comparisons were performed. Data are means ± SE.