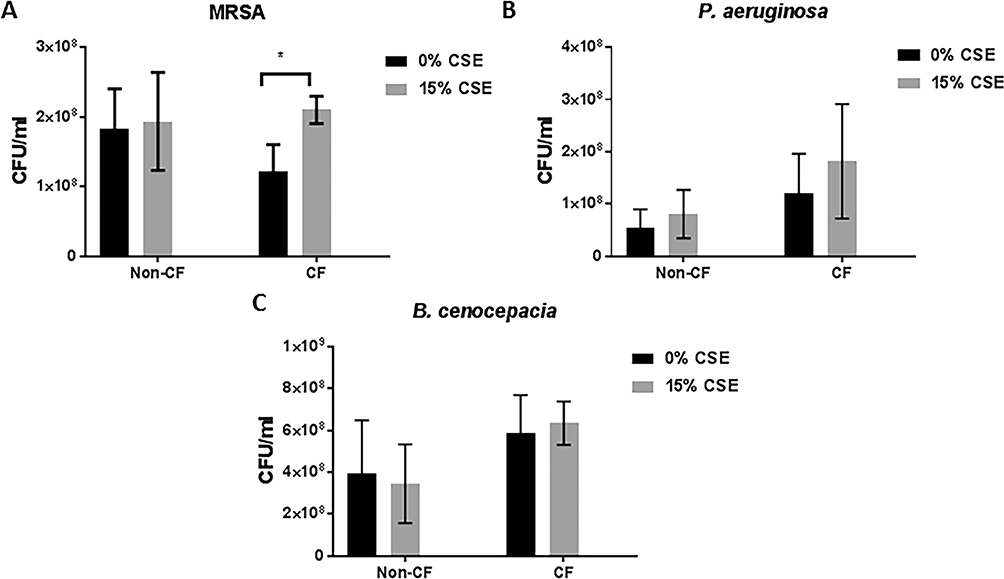
Figure 6.
Secondhand smoke exposure decreases methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) killing in cystic fibrosis (CF) macrophages. Human CF and non-CF macrophages from children and adults were subacutely (72 hours) treated with 15% cigarette smoke extract (CSE) and infected with a clinical isolate of either (A) MRSA, (B) Pseudomonas aeruginosa or (C) Burkholderia cenocepacia, n=6. Bacterial counts were measured via colony-forming unit (CFU) assay and presented as CFU/mL of media.