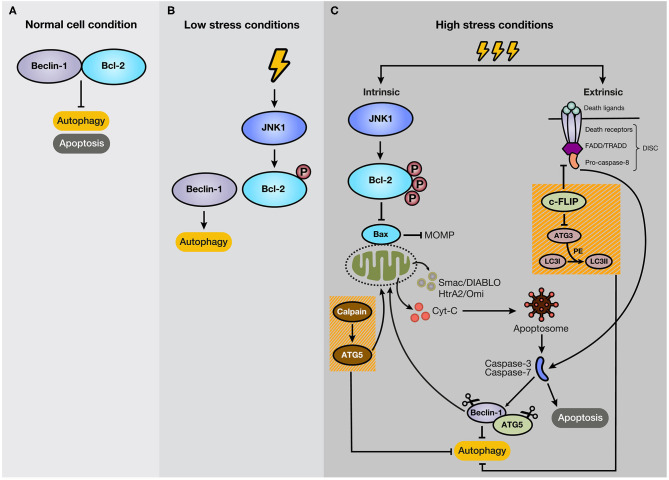
Figure 3.
Mechanism of crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. (A) Under normal cellular conditions, Beclin-1 binds to Bcl-2, keeping autophagy and apoptosis inactivated. (B) However, if the cell experiences low-level stress conditions (e.g., nutrient deprivation), JNK1 phosphorylates Bcl-2, disturbing Bcl-2/Beclin-1 union. As a result, isolated Beclin-1 activates the autophagic pathway. (C) However, if the stressful stimulus crosses a threshold of time, JNK1 promotes Bcl-2 hyperphosphorylation, inducing its dissociation with Bax and the subsequent activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. In addition, c-FLIP, a suppressor of extrinsic apoptosis, also inhibits autophagy through interaction with ATG3, reducing LC3 lipidation. Moreover, caspase activation mediates autophagy-related proteins, such as Beclin-1 and ATG5. Additionally, the C-terminal fragment generated by caspase-mediated cleavage of Beclin-1 translocates to the mitochondrial membrane and stimulates intrinsic apoptosis. Furthermore, ATG5, after cleavage by calpains, suppresses autophagy activity and induces apoptosis.