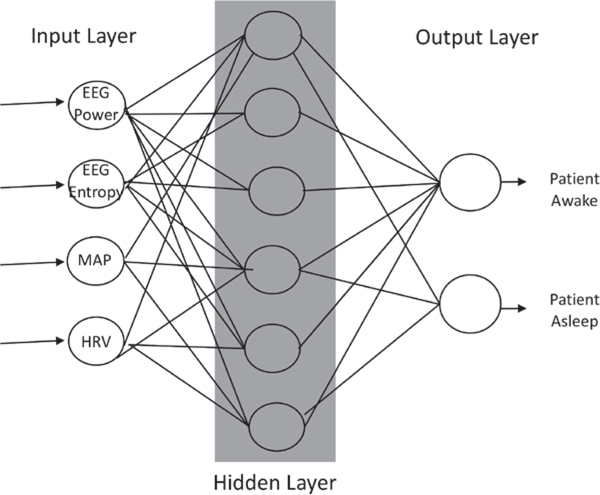
Fig. 4.
An illustrative example of a three-layer neural network. The input layer provides features such as electroencephalogram (EEG) power and entropy, the patient’s mean arterial pressure (MAP), and the patient’s heart rate variability (HrV) to the network. A hidden layer transforms inputs into features usable by the network. The output layer transforms the hidden layer’s activations into an interpretable output (e.g., patient awake vs. asleep).