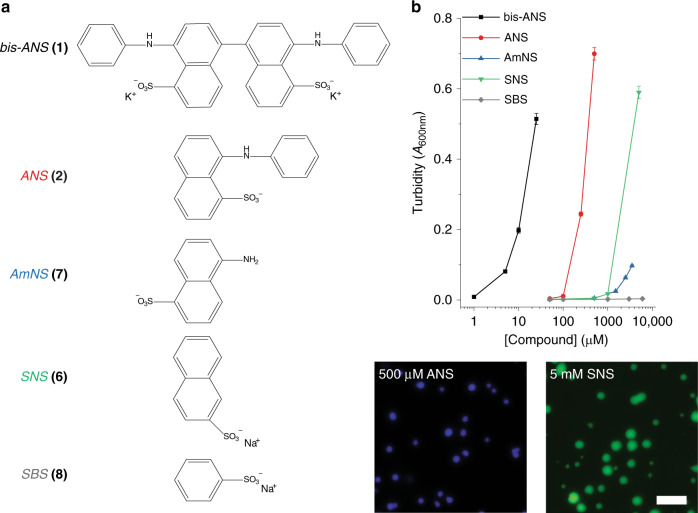
Fig. 4. Comparison of the ability for naphthalene sulfonate derivatives to induce TDP-43 LCD LLPS.
a Chemical structures of naphthalene derivatives: bis-ANS (1), 8-anilinonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid (ANS, 2), 5-amino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid (AmNS, 7), sodium 2-naphthalene sulfonate (SNS, 6), and sodium benzene sulfonate (SBS, 8). b Turbidity as a function of compound concentration for chemicals depicted in panel (a) (top panel) and representative fluorescence microscopy images of droplets formed in the presence of ANS or SNS (bottom panels). Droplets containing SNS were imaged using protein doped with Alexa Fluor 488-labeled TDP-43 LCD. Experiments were performed in a 20 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 6.0, using 10 μM His-tagged TDP-43 LCD. Scale bar: 10 μm. All data are presented as mean values ± standard deviation (n = 3 technical replicates).