Figure 4.
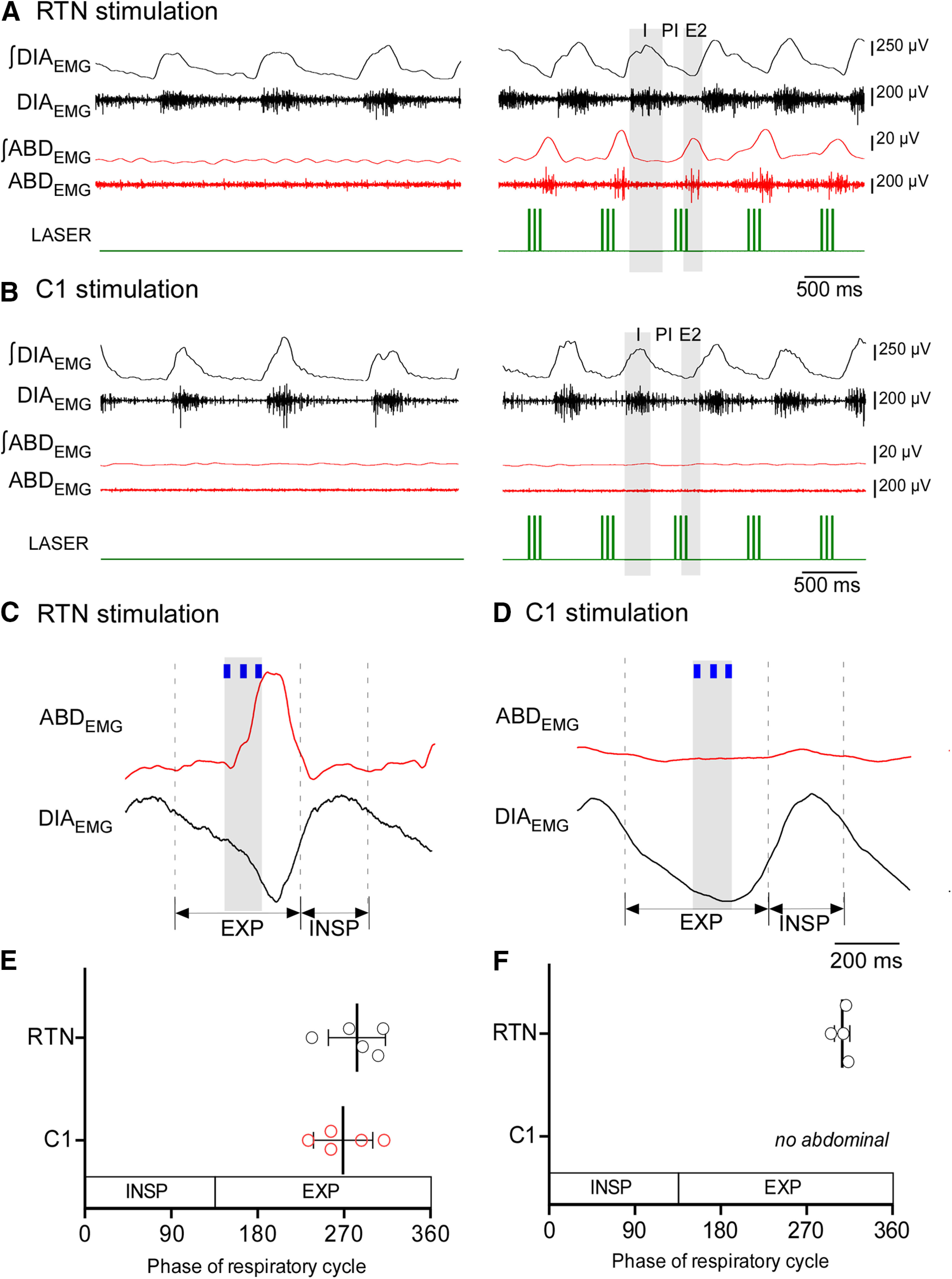
Stimulation of RTN neurons entrains the respiratory cycle and induces active expiration. A, DIAEMG and ABDEMG during phasic stimulation of RTN neurons. Phasic stimulation (1.5 Hz) entrains the respiratory cycle and triggers a burst of ABDEMG in the late-expiratory phase (E2). B, DIAEMG and ABDEMG during phasic stimulation of C1 neurons. C1 phasic stimulation entrains the respiratory cycle but does not elicit active expiration. I, Inspiration; PI, post inspiration (also known as E1 phase); E2, late-expiratory phase. C, Waveform averages of DIAEMG and ABDEMG showing the relationship between the phase of the respiratory cycle and the entrainment stimulus for RTN cases. D, Waveform averages of DIAEMG and ABDEMG showing the relationship between the phase of respiratory cycle and the entrainment stimulus for C1 cases. E, Respiratory cycle represented in 360° showing the phase of the respiratory cycle when stimulus entrains breathing for RTN (n = 5) and C1 (n = 5) stimulation. Student's t test: RTN versus C1, p = 0.4735. F, Phase angle of the ABDEMG peak elicited by phasic RTN stimulation. In 1 rat, phasic RTN stimulation entrained the respiratory cycle but did not activate ABDEMG. In this animal, active expiration occurred only during 20 Hz continuous stimulation.
