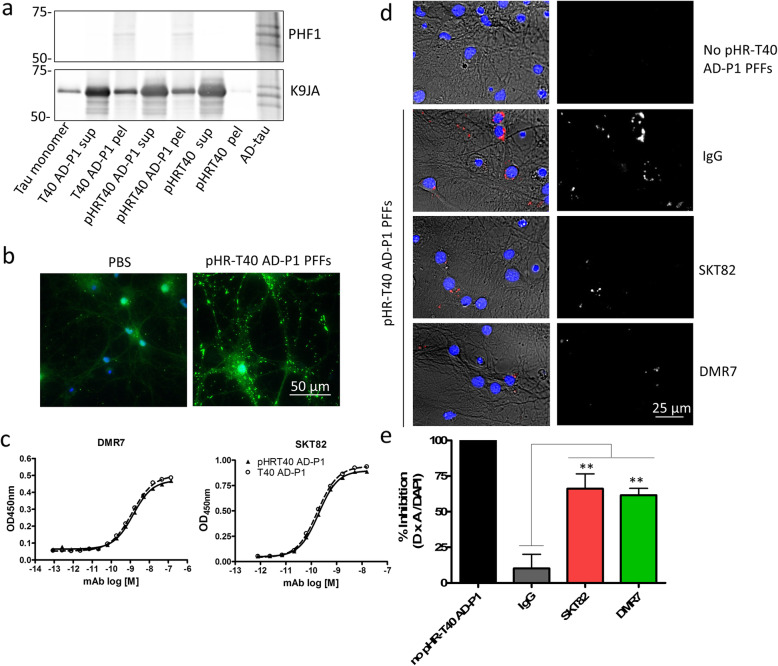
Fig. 5.
Tau mAbs inhibit uptake of tau seeds into primary neurons. a Western blot characterization of AD-tau seeded fibrillization reaction sedimentation following centrifugation of unlabeled tau monomer (T40 AD-P1), pHR-T40 AD-P1 fibrillization reaction, and pHR-T40 monomer lacking AD-tau seeds. T40 tau monomer and AD-tau are included as controls. b Immunocytochemistry staining of mouse-tau specific R2295M antibody (green) demonstrating that pHR-T40 AD-P1 PFFs are capable of seeding pathological tau aggregates in WT primary mouse neurons. c Sandwich ELISA assay of pHR-T40 AD-P1 and T40 AD-P1 PFFs captured by total tau antibody K9JA and detected with varying concentrations of SKT82 or DMR7. d Immunofluorescence of internalized tau fibrils labeled with pH-sensitive pHRodo-red dye that fluoresces in acidic late endo/lysosomal compartments. Left panels: overlay of brightfield, pHR-T40 AD-P1 PFFs red channel, and DAPI nuclei blue channel. Right panelsl: pHR-T40 AD-P1 PFFs red channel converted to white for visualization. e Quantification of fluorescent internalized pHRodo-red-labeled tau fibrils. Non-specific mouse IgG control did not inhibit uptake of fibrils into neurons, whereas SKT82 and DMR7 significantly inhibited the uptake of fibrils into neurons. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc analysis **p < 0.01 compared to IgG control n = 4 biological replicates