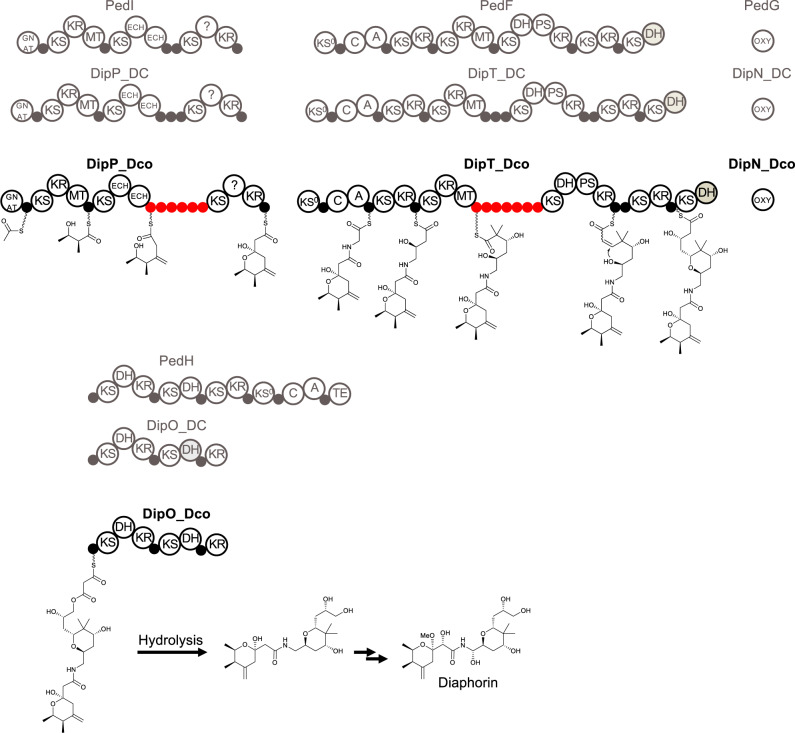
Fig. 3.
Architecture of the PKS proteins from Profftella_Dco (Dip_Dco, shown in bold), with the predicted biosynthetic pathway for diaphorin in Profftella_Dco. For comparison, PKS orthologs from Profftella_DC (Dip_DC) and the Paederus symbiont (Ped) are shown in gray, above Dip_Dcos. A, nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) adenylation domain; C, NRPS condensation domain; DH, dehydratase; GNAT, GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase superfamily (usually serving as acetyltransferase in PKSs); ECH, enoyl-CoA reductase-like domain; KR, ketoreductase; KS, ketosynthase; KS0, nonelongating KS; MT, C-methyltransferase; PS, putative pyrane synthase; OXY, oxygenase; TE, thioesterase; ?, region of unknown function. The domains in gray are predicted to be inactive due to missing active-site residues. The small circles denote carrier protein domains including ACPs and PCPs (NRPS peptidyl carrier proteins). Unusually amplified ACPs in DipP_Dco and DipT_Dco are highlighted in red (see also supplementary text S1, Supplementary Material online).