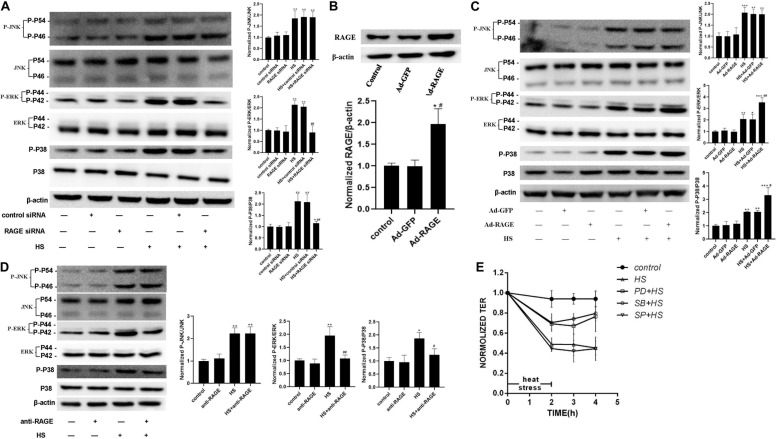
FIGURE 5.
ERK and P38 MAPK involved in the signal pathway by which RAGE involved in heat-induced endothelia barrier dysfunction. (A) HUVECs were treated with either control or RAGE siRNA. Cells were then subjected to heat stress at 42°C for 2 h. Samples were harvested 2 h after heat exposure. The protein expression and phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, and P38 were evaluated by western blot analysis. β-actin was used as a loading control. the phospho/total MAPK is normalized to 1 in the untreated control. (B) Evaluation of transfection efficiency of adenovirus expressing RAGE. Cells were infected with Ad-RAGE or Ad-GFP for 48 h, and total protein was extracted and subjected to western blot to evaluate the expression of RAGE. (C) Cells infected with Ad-RAGE or Ad-GFP were subjected to heat stress at 42°C for 2 h. Samples were harvested 2 h after heat exposure and analyzed by western blot. (D) HUVEC monolayers were treated with heat at 42°C for 2 h after an absence (control) or presence of RAGE antibody for 1 h. Samples were harvested 2 h after heat exposure. The protein expression and phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, and P38 were evaluated by western blot analysis. (E) HUVEC monolayers were treated with heat at 42°C for 2 h after an absence (control) or presence of JNK, ERK, or P38 MAPK inhibitor for 1 h. Samples were harvested 2 h after heat exposure. TEER was recorded before (used as a baseline) and after heat Stress. Values are presented as a percentage relative to that before heat stress (n = 3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs control group, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs HS group).