Table 2.
Association Between Different Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measures (per 20-mm Hg Increase in SBP) or Dipping Status of Nighttime Blood Pressure (per 10% Increase in Nocturnal SBP Dipping) and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
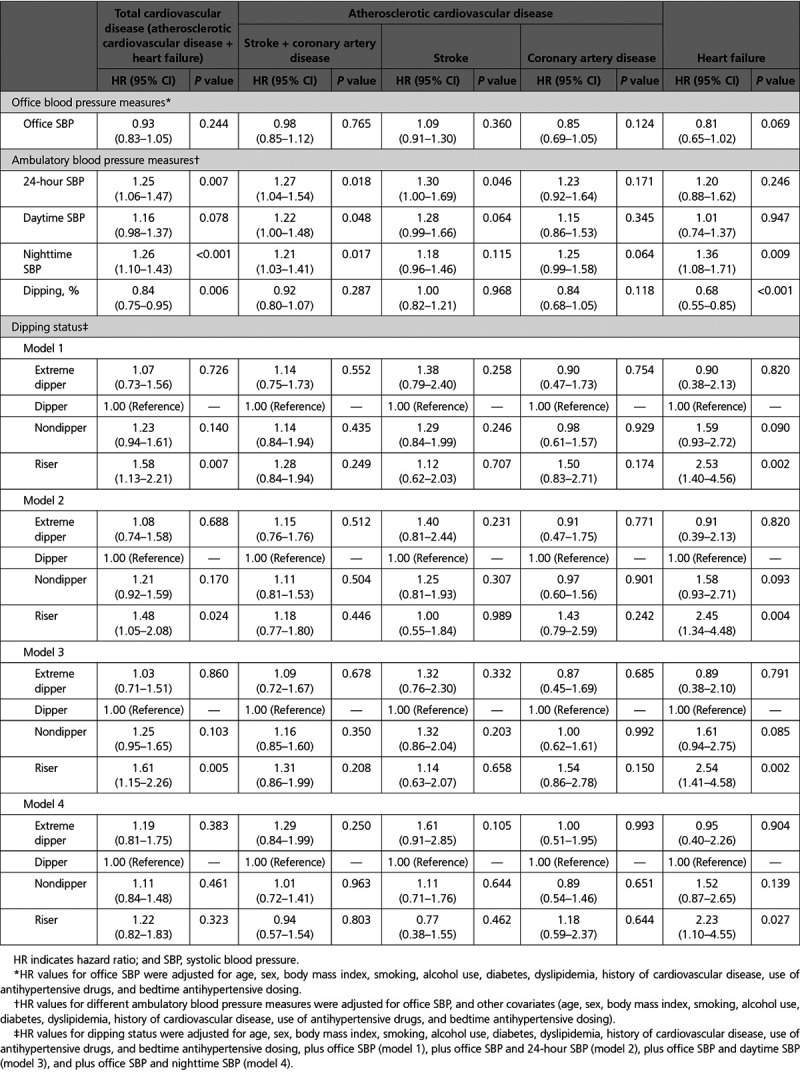
Association Between Different Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measures (per 20-mm Hg Increase in SBP) or Dipping Status of Nighttime Blood Pressure (per 10% Increase in Nocturnal SBP Dipping) and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
