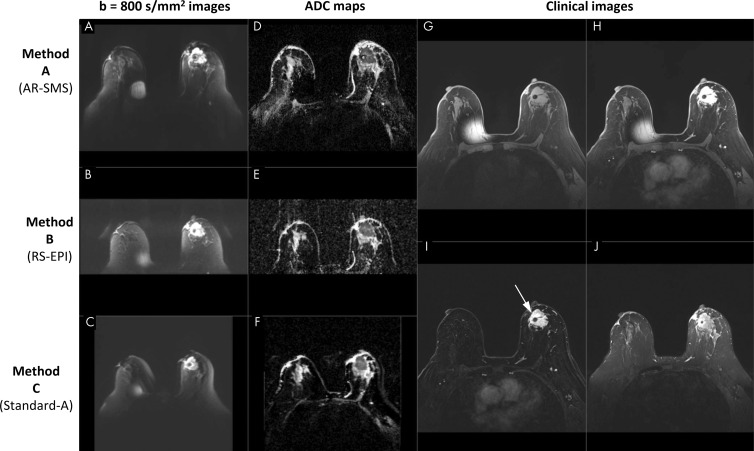
Figure 1:
Screenshot of a picture archiving and communication system setup in a 70-year-old participant with large biopsy-proven cancer. Readers were provided with clinical images, including, G, a noncontrast-enhanced image, H, a single contrast-enhanced image, I, a contrast-enhanced subtraction T1-weighted image, and, J, a T2-weighted image, with the lesion indicated (arrow). Diffusion data included axial images with, A–C, b value of 800 sec/mm2 and, D–F, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps for all three methods, randomly ordered as methods A, B, and C, which are labeled here for illustration purposes. The metal needle of the contrast injection port caused the artifact on the right breast. AR-SMS = axially reformatted–simultaneous multislice, RS-EPI = readout-segmented echo-planar imaging.