Extended Data Fig. 5: HHEX, PDX1 and PROX1 inhibition by retinoic acid receptor antagonist exposure in human boundary organoid and mouse embryo.
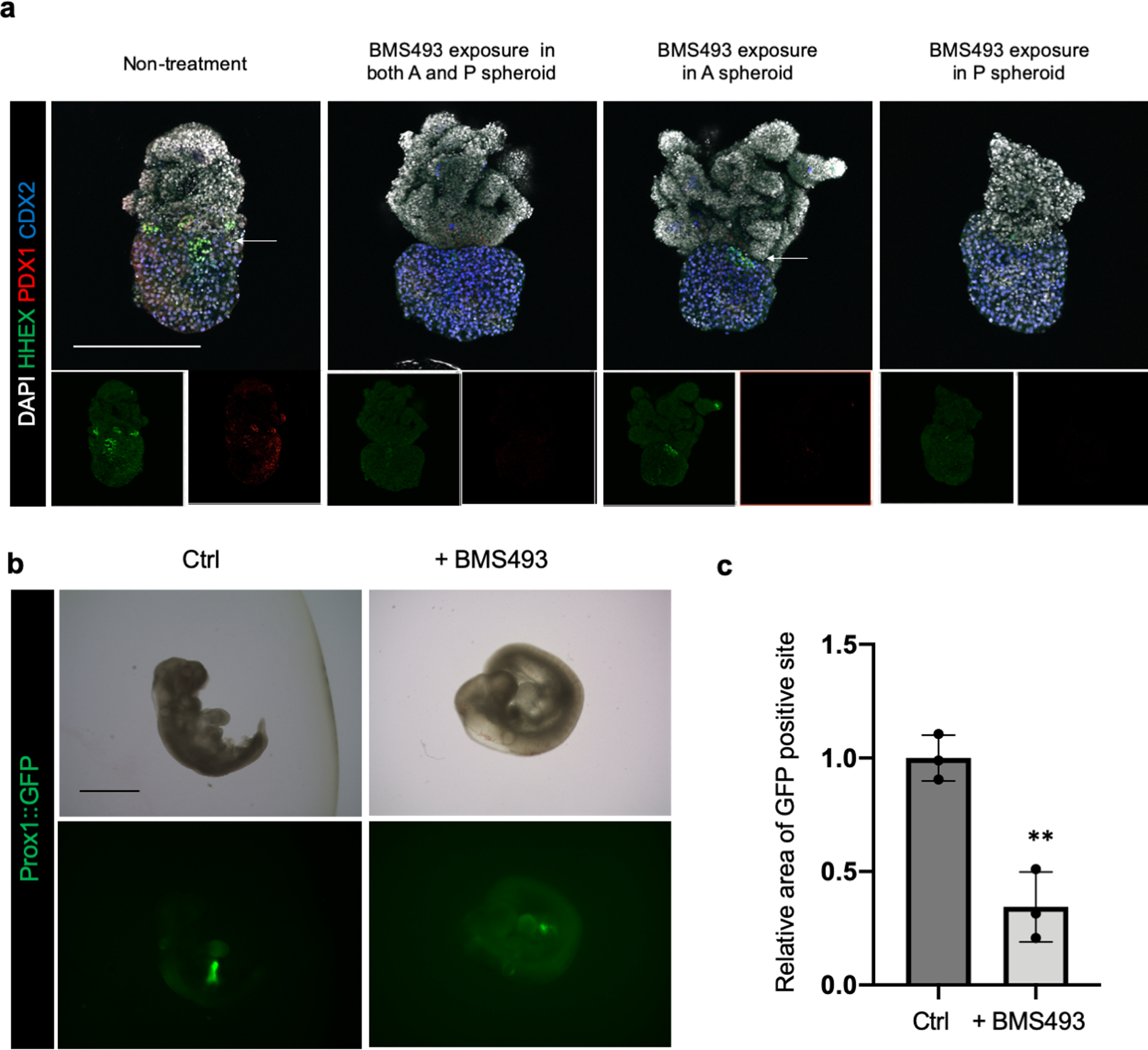
a. Retinoic acid receptor antagonist, BMS493 pretreated anterior or posterior spheroids were fused to induce HBP anlage formation, and wholemount stained for HHEX, PDX1 and CDX2. Compared to untreated control group, the group of BMS493 pretreated posterior spheroid was inhibited HHEX and PDX1 expression at boundary, suggesting retinoic acid receptor function in posterior side was important to establish HBP boundary organoid. Representative of n = 4 independent organoids showing similar results. Scale bar: 200 μm
b,c. Prox1 inhibition by BMS493 exposure with embryonic day (E) 9.0 Prox1::GFP reporter mouse embryo explant culture. The whole embryo was cultured in the rotator-type bottle culture system for 24 hrs. Retinoic acid receptors antagonist BMS493 treated group was compared with control (adding DMSO) group. b. Bright field image and GFP fluorescent image for embryo after culture. Representative of n = 3 independent organoids showing similar results. c. The area of GFP expressing parts were quantified from GFP image in (b). Data were mean ± s.d. (n = 3). P = 0.0035 by Unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bar: 1 mm
