Fig 3. Caffeine-treated rats recovered their righting reflex at a significantly higher isoflurane concentration than did the same rats when treated with saline.
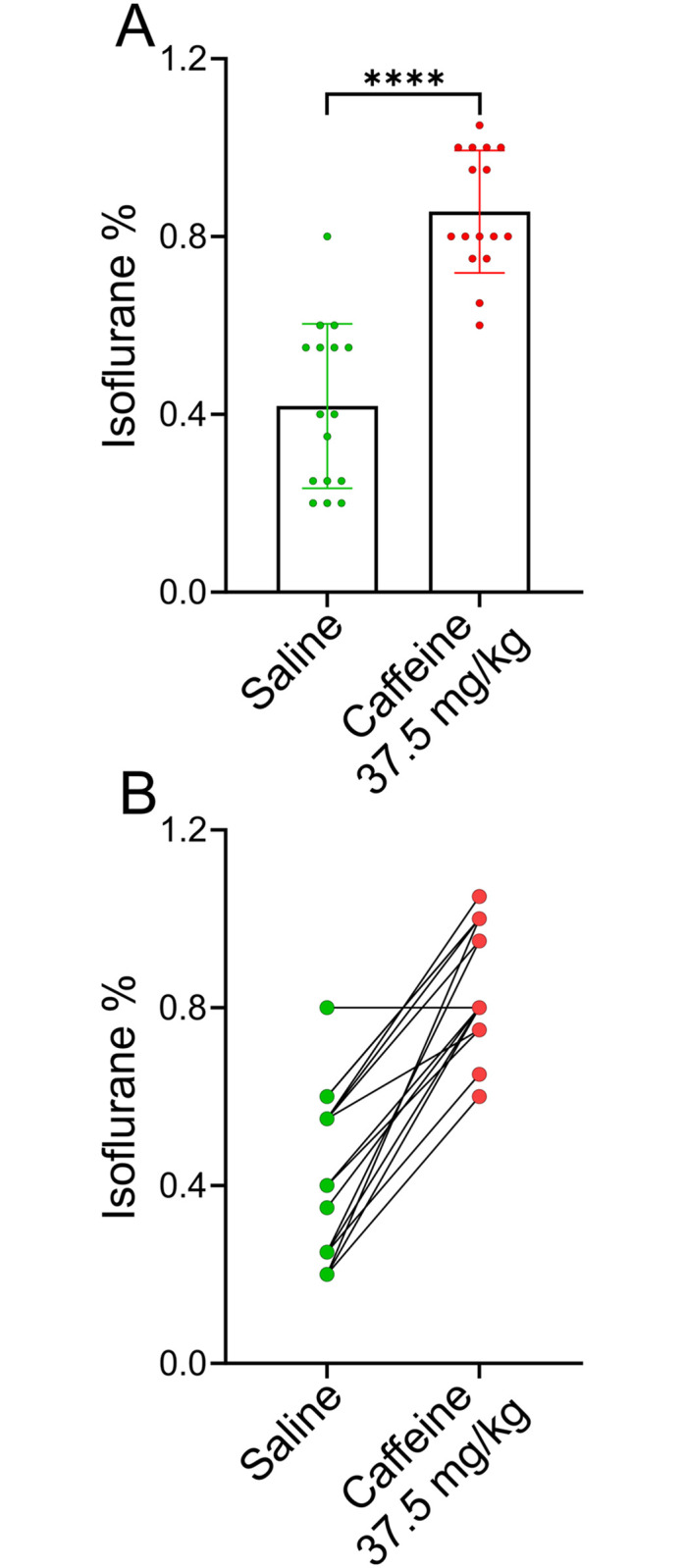
A, A group of 16 adult female rats were anesthetized and then injected with either saline () or caffeine () (37.5 mg/ kg) on two different days. The protocol for determining the isoflurane concentration where rats recovered their righting reflex is described in the Methods section. The order of caffeine or saline was randomized, with 8 rats receiving caffeine on the first anesthesia session and 8 rats receiving saline. The caffeine-treated rats recovered their righting reflex at 0.86 ± 0.14% isoflurane (mean ± SD), while the saline-treated rats recovered their righting reflex at 0.42 ± 0.19% isoflurane, p < 0.0001, n = 16 (paired T-test). B, plots the isoflurane concentrations recorded at RORR for all 16 rats. Symbols in green represent the isoflurane levels recorded at RORR for the saline session, while those in red represent the caffeine session.
