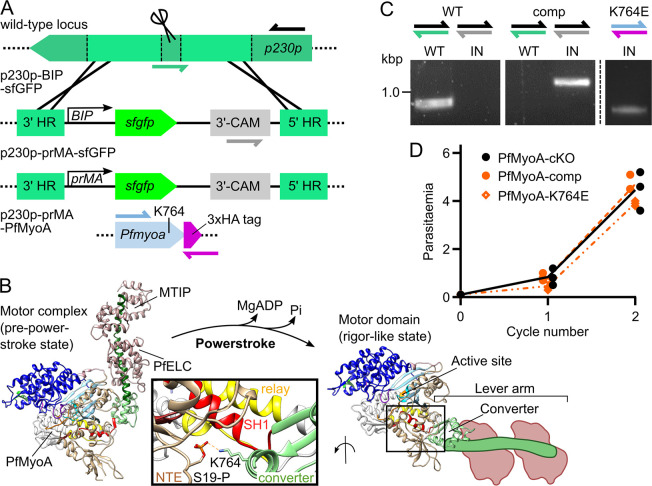
Fig 1. Development of a conditional knockout and complementation system for Plasmodium myosins.
A Schematic of the modified p230p locus. The p230p-BIP-sfGFP repair template introduces sfgfp under a constitutive BIP promoter. The BIP promoter is exchanged for the Pfmyoa promoter, forming p230p-prMA-sfGFP, with sfgfp exchanged for 3xHA-tagged Pfmyoa forming PfMyoA-comp or PfMyoA-K764E. B Myosins produce force during a powerstroke, where conformational changes from ATP hydrolysis are communication by a relay (yellow) and SH1 (red) helices to the converter, to swing the lever arm. The SH1 helix in PfMyoA is unusually immobile and additional interactions are needed to stabilise the rigor-like state. Stabilising residues include those between phospho-S19 in the N-terminal extension (NTE, brown) and K764 in the converter (green). PPS structure from [21]; Rigor-like structure (PDB: 6I7D, neck region and light chain outlines added as schematic, by extension of the last helix of the converter). C Genotyping PCR of PfMyoA-comp and PfMyoA-K764E lines confirmed that the WT p230p locus (green half arrow) is completely lost in PfMyoA-comp, while the integrated locus (IN, grey half arrow) is present. D PfMyoA-comp parasites grow at the same rate as the parental PfMyoA-cKO line, while PfMyoA-K764E parasites grow slightly slower over 96 h. Lines show mean parasitaemia, N = 3, each experiment in triplicate.