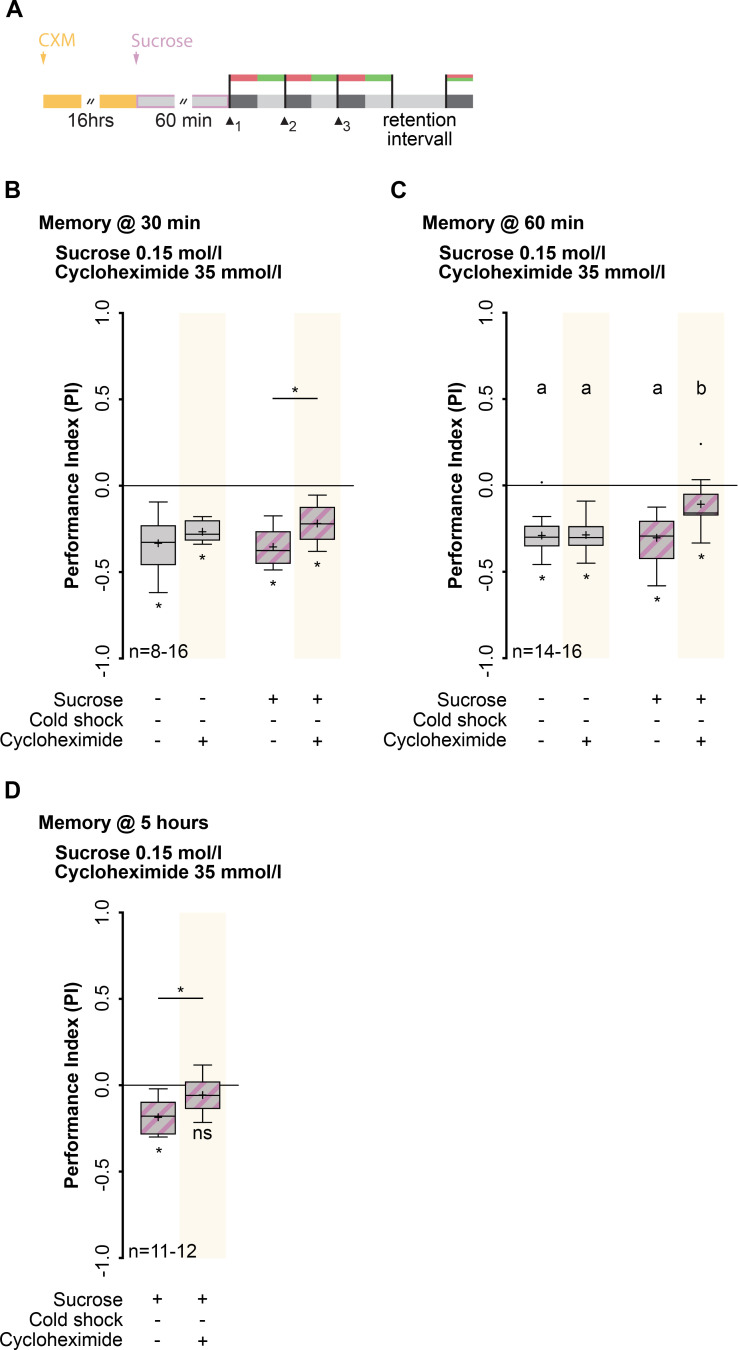
Fig 4. Rapid consolidation of a de-novo protein synthesis dependent memory after the consumption of sucrose.
(A) Training and treatment protocols. Before feeding on sucrose, larvae were fed for 16 hours on cycloheximide (CXM). Memory was tested at different time points after training. (B) Memory tested 30 min after training was only statistically different between larvae that consumed sucrose with or without CXM treatment. (C) Memory tested 60 min after training larvae that consumed sucrose showed only a slight memory after CXM treatment. This memory was statistically significant different to all other groups of larvae. However, it was not completely abolished. (D) The memory formed after sucrose consumption is stable up to 5 hours and is completely abolished in larvae consuming CXM prior to training. For (B) and (C) memory performance above the level of chance was tested using Bonferroni-corrected one-sample t-tests (ns p≥0.05/4; * p<0.05/4; adjusted significance level α). Differences between groups were determined using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc pairwise comparisons and are depicted above the respective box plots. In (B) * indicates p<0.05. In (C) lowercase letters indicate differences between groups (p<0.05). For (D) memory performance above the level of chance was tested using Bonferroni-corrected one-sample t-test (ns p≥0.05/2; * p<0.05/2; adjusted significance level α). Differences between groups were determined using unpaired t-test and are depicted above the respective box plots; * indicates p<0.05). For more statistical details see also S1 Table, S2 Table and S3 Table. Data are shown as Tukey box plots; line, median; cross, mean; box, 75th-25th percentiles; whiskers, 1.5 interquartile range; small circles, outlier (n≥8).