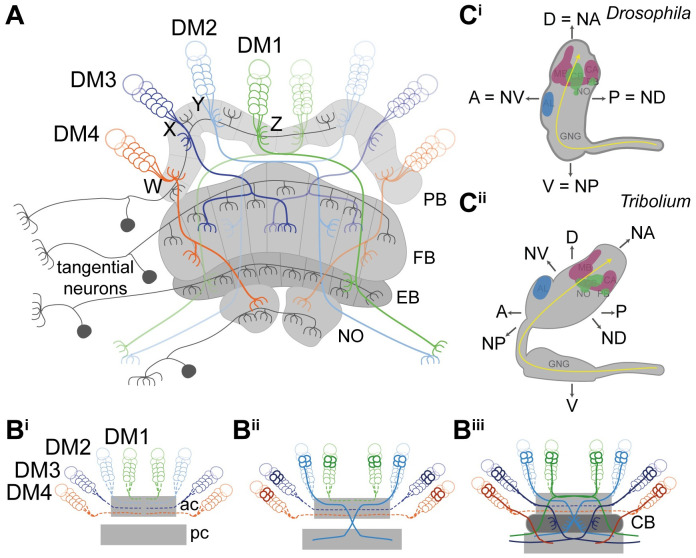
Fig 1. Structure and development of the central complex, and relationship of neuraxis to body axes.
(A) Tangential neurons (dark gray) connect neuropils of the central complex with other areas. Columnar neurons (colored) connect the different neuropils of the central complex with each other. Nearly all columnar neurons derive from 4 type II neuroblasts, DM1-4 (green, light blue, dark blue, orange) that project through WXYZ tracts. (B) Central complex development starts with the neurons of the DM1-4 lineage (alternative names in Drosophila: DPMm1, DPMpm1, DPMpm2, CM4 or in Schistocerca: ZYXW) projecting into an ac (hatched lines in Bi) where they cross the midline and build up a stack of parallel fibers. Later-born neurons (solid lines in Bii) undergo fascicle switching, i.e., they leave the ac-fascicle at stereotypical locations and re-enter a fascicle of a pc, forming X-shaped crossings with neurons from the contralateral side (called decussations) (Bii). Decussations occur at different positions subdividing the future central body into columns (Biii). PB omitted for simplicity; based on [15,22,32,33]. (C) The Drosophila (Ci) and Tribolium (Cii) brains differ in their orientation within the head (lateral views). Although the Drosophila brain is oriented perpendicular to the ventral nerve cord, the Tribolium brain is tilted backwards. This leads to discrepancies when using the body axis as reference. For instance, the AL is anterior in Drosophila, whereas it is more dorsal in Tribolium. Similarly, the PB is posterior in Drosophila but rather ventral in Tribolium. To facilitate cross-species comparisons, we use the classic neuraxis nomenclature as suggested by [34]. In this system, the ALs are n-ventral (NV) and the PB n-dorsal (DV) in both species. Shapes of brains are based on v2.virtualflybrain.org/ and data from this study, whereas the shape of the Tribolium GNG is from [35]. Information about cell innervation in A was taken from [21,25,36]. A, anterior; ac, anterior commissure; AL, antennal lobe; CA, calyx; CB, central body; D, dorsal, DM, dorso-median; FB/EB, upper and lower division of the CB, respectively; GNG, gnathal ganglia; MB, mushroom body (excluding CA); n, neuraxis-referring; NO, noduli; NV, n-ventral; P, posterior; PB, protocerebral bridge; pc, posterior commissure; V, ventral.