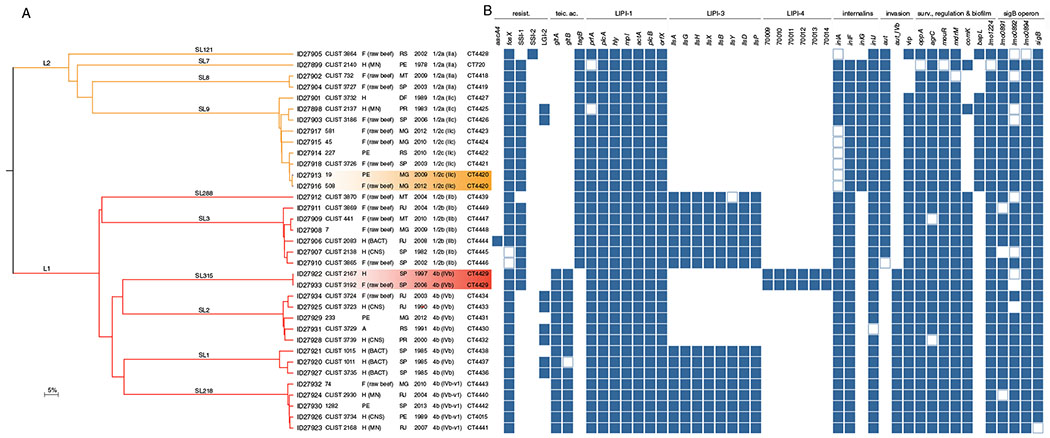
Fig. 2.
Virulence and resistance gene profiles of the 35 isolates sequenced in this study.
A. Single-linkage clustering based on the cgMLST profiles. Branches are coloured by phylogenetic lineage (L1, red; L2, orange) and labelled by SL. Information on the BIGSdb identifier, isolate’s name, origin (H, human; F, food; PE, food production environment), state (PE, Pernambuco; MT, Mato Grosso; SP, São Paulo; RS, Rio Grande do Sul; MG, Minas Gerais; PR, Paraná; DF, Distrito Federal; and RJ, Rio de Janeiro), year of isolation, serotype (serogroup) and CT are provided. B. Resistance and virulence genes patterns of either presence, absence or truncation. Colour-filled boxes represent the presence of the different genetic traits. Empty boxes represent genes with truncations leading to premature stop codons. Absent genes are marked in white. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]