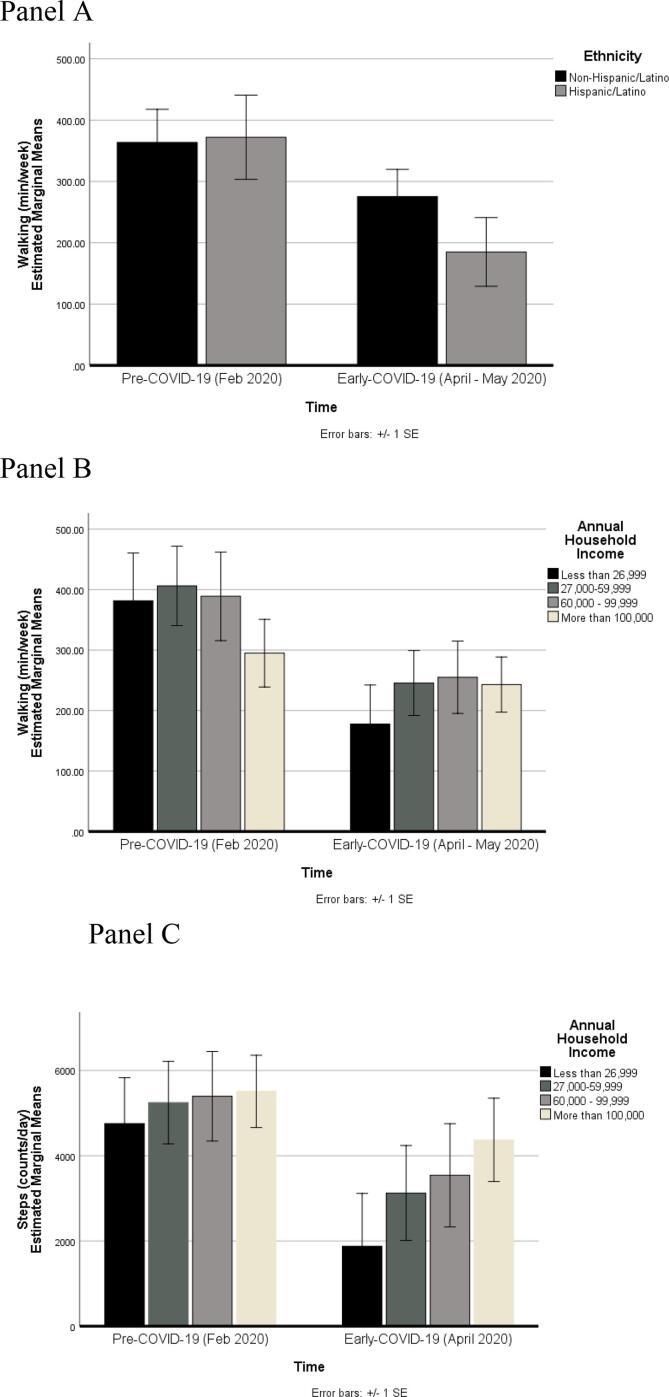
Fig. 2.
Panel A: Effects of time (pre-COVID-19 [Feb. 2020] vs. early-COVID-19 [April-May 2020]) on minutes of walking physical activity per week by ethnicity (Hispanic/Latino n = 57, non-Hispanic/Latino n = 208). Estimated marginal means are presented for raw (untransformed) data adjusting for sex, age, weight status, and annual household income. n = 265. Panel B: Effects of time (pre-COVID-19 [Feb. 2020] vs. early-COVID-19 [April-May 2020]) on minutes of walking per week by annual household income (n = 36 for <$27,000, n = 70 for $27,000–$59,999, n = 48 for $60,000–$99,999, n = 111 for ≥$100,000). Estimated marginal means are presented for raw (untransformed) data adjusting for sex, age, weight status, ethnicity. n = 265. Panel C: Effects of time (pre-COVID-19 [Feb. 2020] vs. early-COVID-19 [April 2020]) on smartphone accelerometer-derived steps per day by annual household income (n = 23 for <$27,000, n = 38 for $27,000–$59,999, n = 23 for $60,000–$99,999, n = 59 for ≥$100,000). Estimated marginal means are presented for raw (untransformed) data adjusting for sex, age, weight status, and ethnicity. n = 143.