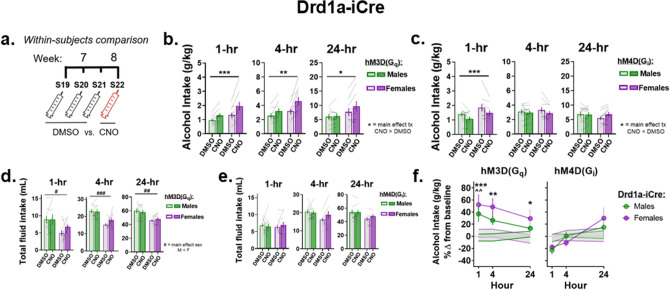
Figure 5.
NAc D1-MSNs bidirectionally control alcohol intake within Drd1a-iCre rats of both sexes. (a) Timeline of DMSO and CNO administration. Sessions 19–21: DMSO was administered 30-min before the start of each alcohol session, and bottles were weighed 1-, 4-, and 24-h after the start of drinking. Session 22: CNO was administered to the same rats that received DMSO during sessions 19–21 30-min before the start of drinking, and bottles were weighed 1-, 4-, and 24-h later. (b) CNO administration to Drd1a-iCre rats expressing the hM3Dq DREADD increased alcohol intake 1-, 4-h, and 24-h after the start of alcohol-drinking compared to when the same rats were administered DMSO during week-7. (c) Drd1a-iCre rats expressing the hM4Di DREADD displayed a reduction in alcohol intake 1-h after the start of drinking when administered CNO compared to DMSO. (d,e) Total fluid intake after CNO administration compared to total fluid intake after DMSO administration was unaltered regardless of time and DREADDs virus. Drd1a-iCre male rats expressing hM3Dq showed significantly increased total fluid intake compared to females. (f, left.) When collapsed by sex, Drd1a-iCre rats with the hM3Dq DREADD displayed significantly increased percent changes in alcohol intake compared to Wt rats that received the hM3Dq DREADD infusion across all three time points measured. When separated by sex, this increase was apparent in Drd1a-iCre males 1-h after the start of drinking compared to 1-, 4-, and 24-h in Drd1a-iCre females. (f, right.) No significant percent changes in alcohol intake were observed when comparing Drd1a-iCre rats expressing hM4Di to Wt rats that received hM4Di. Data represented as mean ± SEM (b–e) main effect of treatment *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; main effect of sex #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001. (f) Females *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; Males ^^p < 0.01.