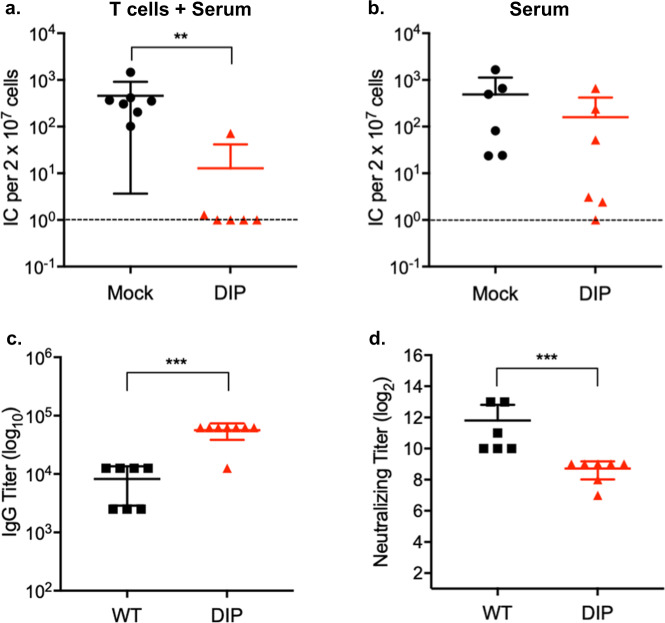
Fig. 6. DIP vaccination elicits protective antibodies.
Mice were intraperitoneally infected with 105 PFU WT or DIP 2 mo previously. a Total T cells and sera isolated from mock- or DIP-infected mice were transferred to congenic naïve mice by tail vein and intraperitoneal injections, respectively. Recipient mice were intranasally challenged 24 h later with 5 × 103 PFU WT virus. Latent infection in the spleen at 14 d post-challenge was assessed by infectious center assay. b Sera collected from uninfected- or DIP-infected mice were transferred to naïve mice that were intranasally challenged 24 h later with 5 × 103 PFU WT virus. Latent infection in the spleen at 14 d post-challenge was evaluated by infectious center assay. c, d Sera collected from infected mice were analyzed for virus-specific IgG by ELISA and for neutralizing activity. Pooled data from 2 independent experiments using different numbers of mice for each replicate. Means and SD indicated by error bars were plotted. Statistical significance was analyzed by a two-tailed Student’s t-test. P < 0.05*, P < 0.01**, P < 0.001***, and P < 0.0001****.