Extended Data Fig. 9: A site-specific recombination-based approach to rescue phenotypes associated with loss of the E-repeat.
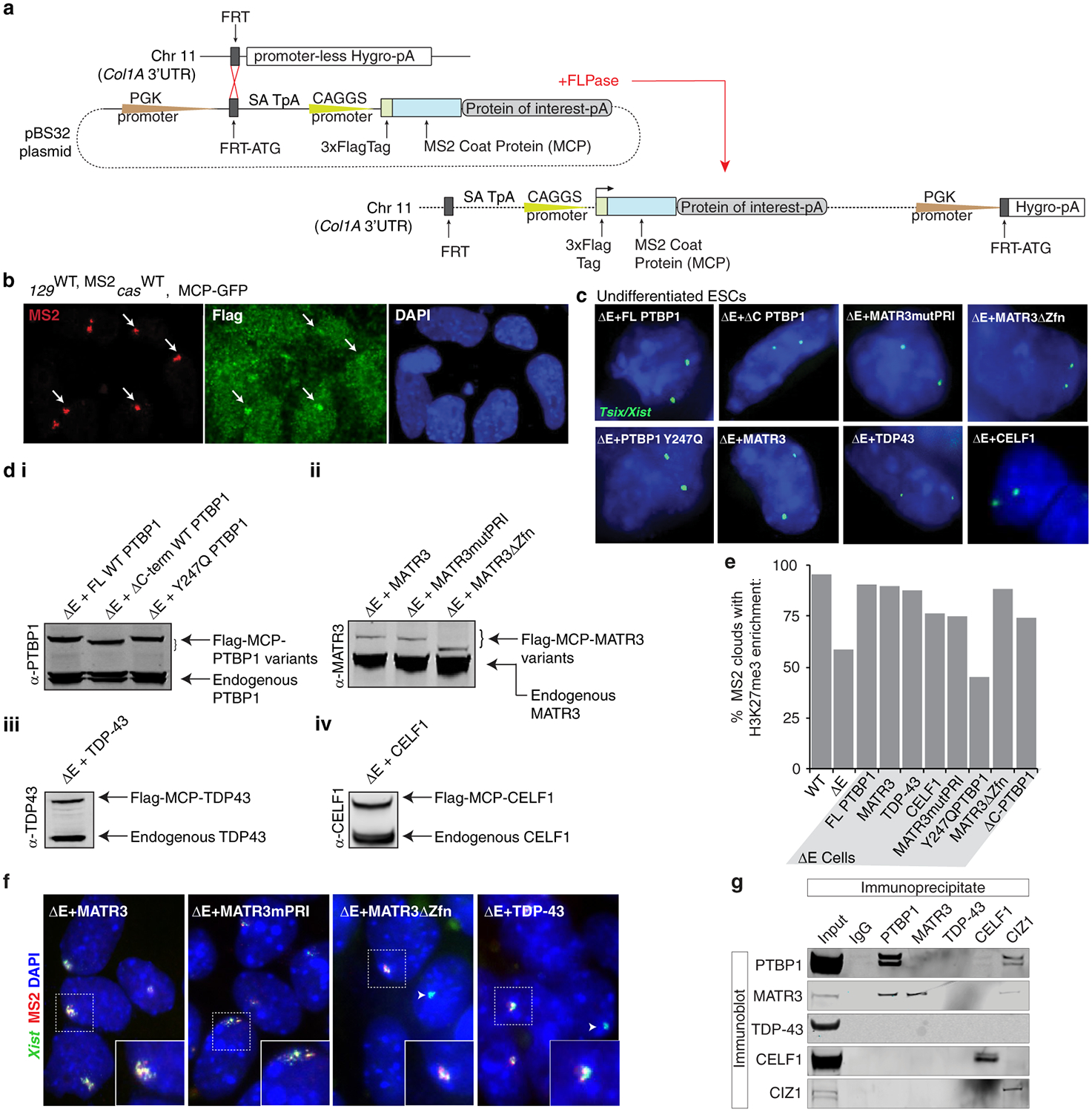
a, Flp-In approach taken to constitutively express Flag-tagged MCP fusion proteins in ESCs (methods). The Flag-MCP-GFP fusion protein was only expressed in WT ESCs. All other rescue constructs were expressed in ΔE ESCs.
b, Flag-MCP-GFP fusion protein recruitment to MS2+Xist in WT ESCs at differentiation day 7 shown with representative epifluorescence images. Arrows indicate MS2+Xist129 clouds with co-localizing Flag-MCP-GFP enrichment.
c, Tsix expression was used as a proxy to confirm presence of two X-chromosomes in rescue ESC lines.
d i, PTBP1-probed immunoblot on lysates from undifferentiated ΔE-ESCs expressing full-length MCP-PTBP1 or MCP-PTBP1 mutants. ii, as in (d-i) except for MATR3 immunoblot for various MATR3 rescue lines. iii, TDP-43-probed immunoblot on lysates from undifferentiated ΔE-ESCs expressing MCP-TDP-43. iv, CELF1-probed immunoblot on lysates from undifferentiated ΔE-ESCs expressing MCP-CELF1.
e, Histogram of the percentage of MS2+Xist clouds that also show enrichment of H3K27me3 in WT or ΔE cells, or ΔE cells expressing the indicated MCP-fusion protein at differentiation day 7 (n=80, from one experiment).
f, Representative epifluorescence images of RNA FISH against Xist (green) and MS2 (red) in day 7 differentiated ΔE cell lines expressing the indicated variants of MCP fusion proteins. Inset: enlargement of marked area. Arrowheads indicate WT Xist clouds in ΔE cells, derived from the cas allele.
g, Immunoprecipitation of PTBP1, MATR3, CELF1, TDP-43 and CIZ1 from ESC nuclear extracts (RNase treated) and detection of co-precipitated proteins with the same antibodies by immunoblotting (to go with Fig. 3f).
For images in d and g, see Supplementary Fig. 1 for source data.
