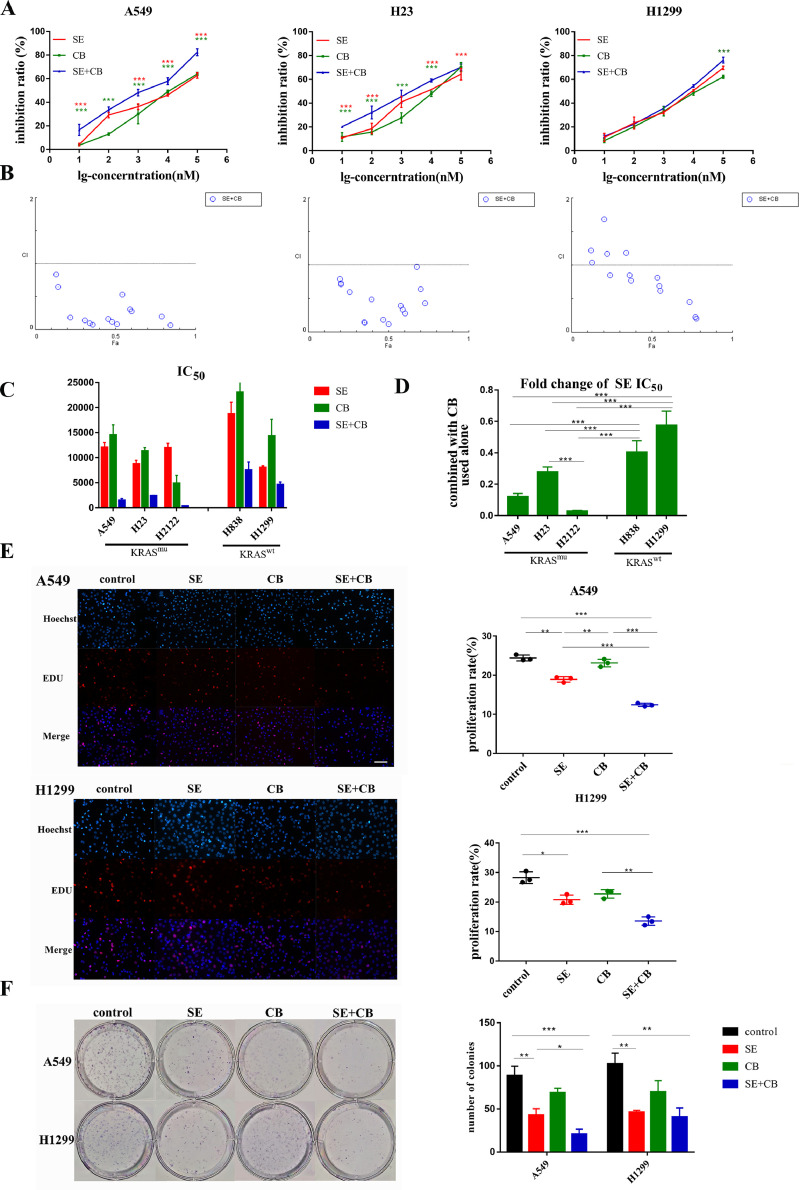
Fig. 2.
CB839 synergized with selumetinib to inhibit proliferation of KRAS-mutant NSCLC cells. KRAS-mutant cells A549, H23, H2122 and the KRAS wild-type cell line H1299, H838 were treated with selumetinib, CB839, or a combination of both at escalating doses that ranged from 10 to 105 nM for 72 h. Subsequent cell proliferation experiments were carried out according to the following combinations and drug doses: control, selumetinib (SE, ½IC50 concentration), CB839 (CB, IC10 concentration), and selumetinib+CB839 (SE ½IC50 concentration +CB IC10 concentration). (A) CCK8 assay of A549,H23 and H1299 cells treated with monotherapy or a combination of selumetinib and CB839. (B) The combination index (CI) plots of selumetinib and CB839 in A549, H23, and H1299 cells. CI values <1 indicated a synergistic drug-drug interaction,CI values <0.3 indicated a strong synergistic effect. (C) IC50 of selumetinib, CB839 alone, and selumetinib combined with CB839. (D) Fold change of IC50 of selumetinib when combined with CB839. (E) Edu assay of cell proliferation of A549 and H1299 cells to test the short-term response to the combination therapy. (200x) (F) The colony formation assay of A549 and H1299 cells to test the long-term response. CI were presented as median (P25, P75), other data were presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. A p-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant (*p<0.05, **p<0.01,***p<0.001;* in red: compared with SE group, * in green: compared with CB group).