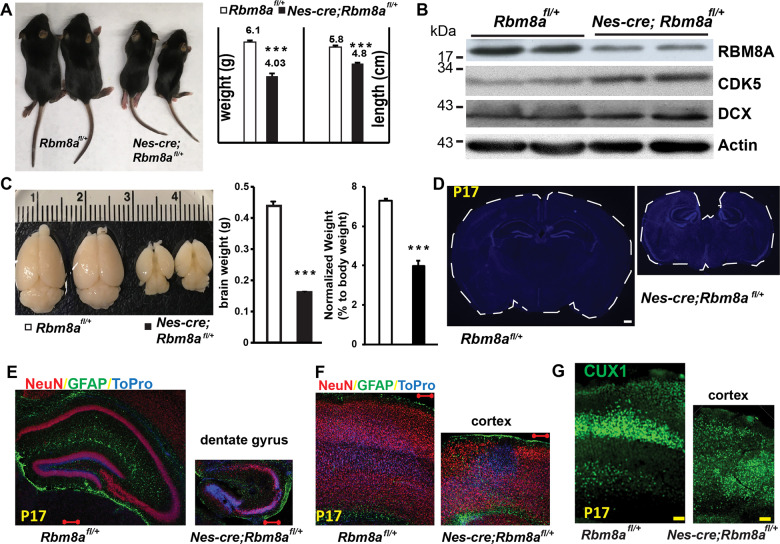
Fig. 1. Rbm8a haploinsufficiency modulates brain size.
A Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ mice are smaller than littermate controls at P17 in both body weight and length. ***p = 5.4 × 10−5 (weight), p = 1.4 × 10−4 (length), n = 3, Student’s t test. B Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ mice show an ~50% reduction in RBM8A protein expression in the brain, as determined by Western blot. They have ~50% more CDK5 protein expression. C Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ mice at P17 suffer from microcephaly (small brain), even when normalizing for their smaller body size. A ruler is included to show the actual brain size. ***p = 1.9 × 10−5 for brain weight and p = 2.6 × 10−4 for normalized brain weight, n = 3, Student’s t test. D Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ mice have a smaller brain than Rbm8afl/+ controls, and have cortical hemispheres that fail to meet at the midline, causing a large gap between the two cortical hemispheres. DAPI staining of coronal brain slices at P17. Scale bar = 50 µm. E P17 hippocampus of Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ mice and littermate controls stained for mature neuronal neuronal marker NeuN (red), reactive astrocyte marker GFAP (green), and DNA marker DAPI (blue). F P17 cortex stained for NeuN (red), GFAP (green), and DAPI. Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ mice have a thinner cortex and less cell dense cortex. G Coronal sections of P17 Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ and Rbm8afl/+ mice brains were immunostained for the superficial layer marker CUX1. Scale bar, 100 µm. Nes-cre; Rbm8afl/+ mice had an abnormal distribution CUX1 (stains deep layers in the medial cortex).