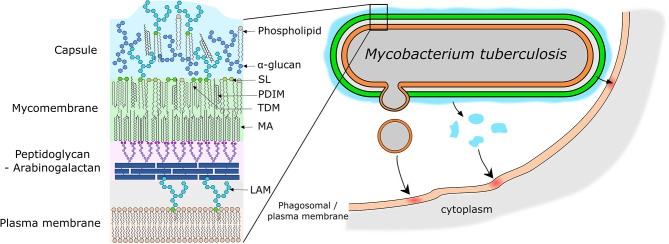
Figure 3.
Models of mycobacterial envelope and lipid transfer. (Left) Simplified model of the organization of the mycobacterial envelope with the main virulence lipids highlighted. (Right) Representation of the different potential mechanisms of lipid release and transfer to the host cell membrane. Lipids can be release by emission of membrane vesicles, or by shedding of the capsular layer into the phagosome lumen or due to close physical contact directly into the phagosome membrane. SL, Sulfolipids; PDIM, Phthiocerol Dimycerosates; TDM, Trehalose Dimycolates; MA, Mycolic Acid; LAM, Lipoarabinomannan.